With Activation, build Flows and metrics to efficiently transform application events into measured user journeys (Flows) and actionable user experience insights, connecting user engagement, experience quality, and technical performance.
-
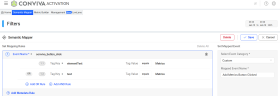
Semantic Mapper: enables raw event mapping and customization so user actions and activities are easy to analyze. Activation simplifies event organization and identity mapping to help explore and manage the ingested application events for enhanced insights, such as mapping login activities across multiple application platforms to a single login event.
After setting up mapping rules, the data pipeline supports continuous mapping, automatically mapping newly added raw events based on the configured the mapping rules. For more details, see Map New Events.
-
Metric Builder: enables creating flows and custom metrics associated with specified initial/follow-up events to analyze data for complex user actions and app performance scenarios. Use Conviva predefined metrics for quick metric creation or map raw events with Semantic Mapper for specialized metrics.
-
Flows: captures expected positive user outcomes for specific tasks within an application, such as login, search, or payment. The flow quantifies the success rate, duration and number of attempts of the User Flow. For more details, see Flows.
-
Custom Metrics: associates with specified initial/follow-up events to analyze data for complex user actions and app performance scenarios. For more details, see Individual Metrics.
-
|
Click to Preview Semantic Mapper |
Click to Preview Metric Builder |
Click to Preview Flows in Trends |
|

|
|
Note: DPI provides a robust set of metrics to enable application performance monitoring and user behavior analysis across the web and native applications. Metric values appear as time series and distributions in metric widgets, and alongside dimensional values in the dimension drill-down tables. Selecting different metric widgets changes the metrics in the dimension tables. All metrics are calculated during the selected time interval. For more details, see DPI Metrics.
What's New in Activation
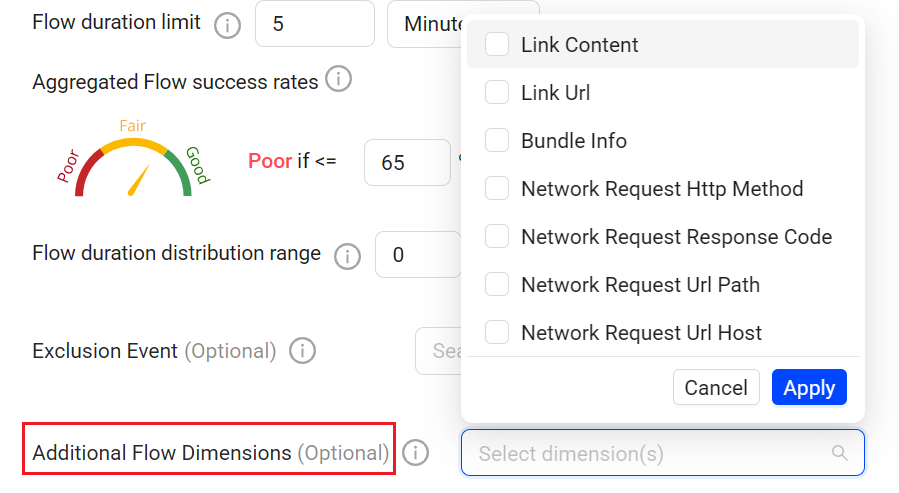
 Metric Builder: Adds an Option for Additional Dimensions in Flows and Custom Metrics Settings(January 2026)
Metric Builder: Adds an Option for Additional Dimensions in Flows and Custom Metrics Settings(January 2026)
|
|
Feature Update:
Adds support for additional event-based dimensions, beyond the out-of-box dimensions, for Flows and custom metrics. Specify whether the dimension value is based on the first-observed event value or the last observed event value, enabling more control of the dimensional values for richer analysis of the configured Flows and custom metrics.
Click to expand the image
Use Case:
Enhance Checkout Flow analysis with the payment_method dimension.
Use the last observed event as the dimension value as payment_method is reported on intermediate events within the checkout flow from Checkout Start to Receipt Page Viewed, rather than only at the Flow start or complete events.
This enhanced flow-level analysis by payment method enables identification of conversion drop-offs, error patterns, and performance differences based on payment types, supporting more targeted optimization and troubleshooting of the payment processes related to the Flow.
More Details: Flows and Custom Metrics.
 Custom Dimension: Promotion of Event Tags to Global Tags (January 2026)
Custom Dimension: Promotion of Event Tags to Global Tags (January 2026)
|
|
Feature Update:
Adds support for promoting event tags as a global dimension across all relevant events, enabling an existing event-level tag to function as a global tag across all relevant events. This update makes it easy to update an event tag to persist across dimensions when a tag represents global context.
Note: Global tags are commonly for user levels or environment data that apply to the current event and all future occurrences of the event until cleared by session or Flow instance.
Click to expand the image
Use Case:
When adding a custom dimension, promote the AccountStatus tag key as a global dimension to perform dimensional analysis of account-related activity, such as page views, clicks, and purchases, across different account status values, including upsell, silverPlan, and goldPlan.
This enhanced analysis by account status helps identify how user behavior, engagement, and conversion patterns vary across subscription tiers, enabling more targeted optimization and troubleshooting.
More Details: Semantic Mapper.
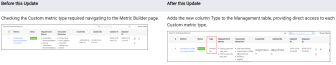
 Activation: Adds a Type Column to the Management Tab (December 2025)
Activation: Adds a Type Column to the Management Tab (December 2025)
|
|
Feature Update:
Adds support for displaying the Custom metric type in the Management tab of Activation. This improvement enables quick confirmation of the metric type, such as conversion, interval, and duration, for each Custom metrics while viewing the other metric settings.
Click to expand the image
Use Case:
Quickly confirm a Custom metric type, such as a conversion, interval, or duration metric, to fully understand the type metric data and deployment status.
More Details: Management.
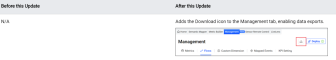
 Activation: Enables Management Data Downloads (December 2025)
Activation: Enables Management Data Downloads (December 2025)
|
|
Feature Update:
Adds support for exporting Management data in xlsx format, enabling easier auditing of Activate changes.
Click to expand the image
Use Case:
To quickly group Custom Metrics by different usage patterns, download the data from the Management tab and sort the data in pivot tables.
More Details: Management.
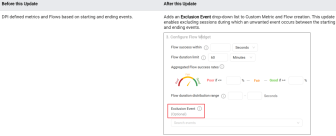
 Flow and Metric Creation: Enables Transition Event Exclusion (November 2025)
Flow and Metric Creation: Enables Transition Event Exclusion (November 2025)
|
|
Feature Update:
Adds support for excluding transition events, enabling metrics and Flows based on user progression from Event A to Event C, without the occurrence of Event B. This feature enables refined insights based on more selective event progressions that eliminate unwanted transitional events.
Click to expand the image
Use Case:
Define a metric that tracks progressions from event A to event C while excluding sessions during which a transition event B occurs.
For example, measure login start to login success accurately, without considering account creation during the flow that may inflate the duration of login metrics.
More Details: Flows and Custom Metrics.
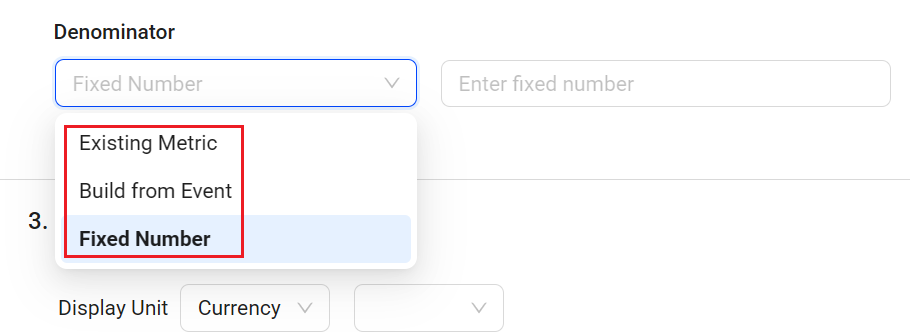
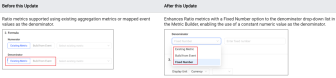
 Metric Creation: Enhances Ratio Metric with Fixed Number as Denominator (November 2025)
Metric Creation: Enhances Ratio Metric with Fixed Number as Denominator (November 2025)
|
|
Feature Update:
Enhances Ratio metrics to support using a fixed number as the denominator, expanding the flexibility and applicability of Ratio metrics.
Click to expand the image
Use Case:
Use the fixed number as a Ratio metric denominator to create Ratio metrics for analyzing revenue across currencies, such as euros based on U.S. dollar data. Apply the current USD-to-EUR exchange rate as the fixed denominator to calculate the Ratio metric for common currency analysis.
More Details: Custom Metrics.
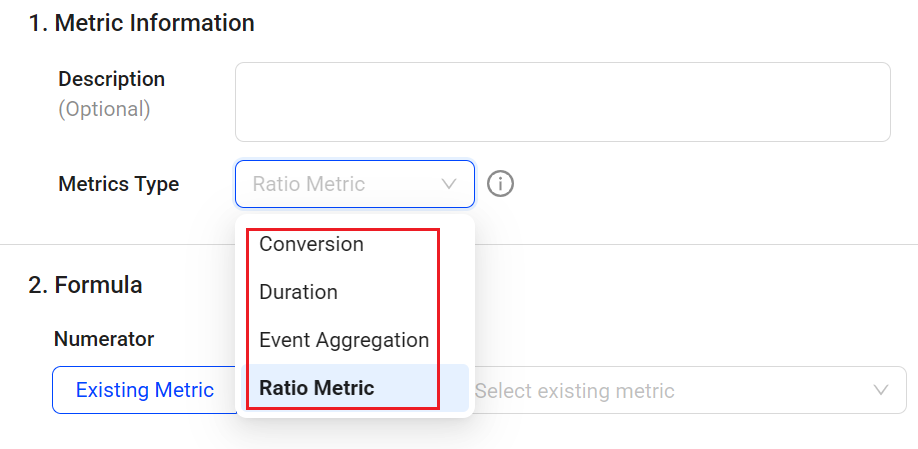
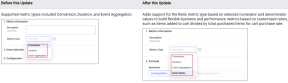
 Individual Metric Builder: Adds Support for Ratio Metrics (October 2025)
Individual Metric Builder: Adds Support for Ratio Metrics (October 2025)
|
|
Feature Update:
Adds a new Ratio metric type in the Individual Metric Builder to build metrics that display the relationships or proportions using mapped event values and OOB/custom aggregation metric values, such as average order value and average session starts to checkout complete. The Ratio metric type provides an additional level of analysis in Trends, such as analyzing the rate of how many orders were made relative to how many page visits occurred. Ratio numerator and denominator values support event counts, average values, and total values from mapped events.
Click to expand the image
Use Case:
Use the Ratio metric type to analyze app performance and user activity based on customized numerator and denominator values to compute rates or averages. For example, to measure the average amount of money a customer spends, create a Revenue Per Paying User metric by selecting the related event and metric to calculate the ratio of Total Revenue to Unique Users, and then view the metric in Trends for dimensional analysis.
More Details: Custom Metrics.
Individual metrics are associated with specified initial and follow-up events that defined the measured start and end points. Use these metrics to analyze data for customized user actions and app performance scenarios, such as analyzing the amount of time spent between login start and completion, and measuring the success rate of cart uploads to completed checkout.
Initial and follow-up event mappings can be defined using Conviva predefined events, custom mapped events, or a combination of both. DPI enables different types of individual event-based metrics.
-
Duration Metric: Measures the time interval between two events.
-
Conversion Metric: Measures the count or conversion rates of events from one stage to another.
-
Event Aggregation Metric: Measures the number of events, or calculates the value of event attributes.
Note: DPI also provides a robust set of metrics to enable application performance monitoring and user behavior analysis across the web and native applications. For detailed definitions of each out-of-box metrics, see Metrics.
 Create Individual Metrics
Create Individual Metrics
Event-based metrics support duration, conversion, and event aggregation type metrics for measuring user experienced based on events and event combinations. Create event-based metrics in Trends and Activation.
-
Start with the location:
-
Activation Home Page
-
Metric Builder
-
Select metric page in Trends
-
-
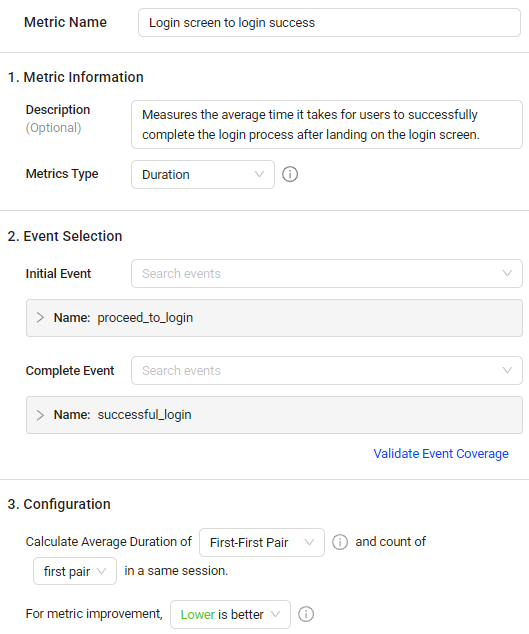
Enter the metric name, and provide the metric information.
-
(Optional) Metric description.
-
From the Metric Type list, select the desired metric type.
-
Conversion Metric: Measures the count or conversion rates between eventsr, such as the count of sessions with successful login after opening the login screen to measure the successful login conversion and find highlights to improve user experience.
-
Duration Metric: Measures the time interval between two events, such as the duration between the login screen event and the login success event to measure login durations and quickly respond to impacting login issues.
-
Event Aggregate Metric: Measures the number of events, or calculates the value of event attributes, such as the average duration of network requests, such as the average duration of network requests to measure the network request performance and do optimization accordingly.
-
-
-
Identify which events to select:
 Check Predefined Events
Check Predefined Events
Predefined events include Conviva predefined events and events that are already mapped. Creating custom metrics based on these predefined events can often save time.
Check the predefined events from the drop-down list for event selection. For example, to analyze the registration process and identify bottlenecks, review the predefined events in the drop-down list. Look for events that indicate the start of registration and successful completion.
For the details of Conviva predefined events, check Out-of-Box Events.
Note: To update predefined events, clone them first, then configure the tag keys and values.
 Discover New Events with EventLooker and LiveLens
Discover New Events with EventLooker and LiveLens
In most cases, predefined events may not fully meet metric creation requirements. Need to map the required events and create metrics based on the newly mapped events.
Use the tools to check raw events and map the events for requirement:
-
EventLooker: Allows browsing and searching events and tag keys. Use the drop-down list to apply a selected event.
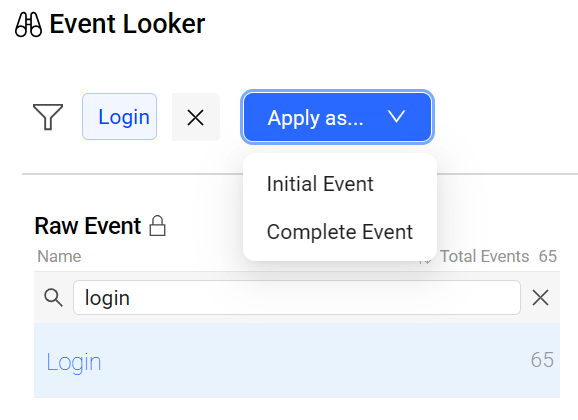
-
LiveLens: Provides real-time event names and tags while interacting with an application. To learn how to use LiveLens, see LiveLens.
-
-
Select the events based on the Metric Type selection and configure metric details based on the selected metric type.
 For Conversion metrics
For Conversion metrics
-
Select events:
-
Initial Event: This refers to the initial event as defined previously.
-
Complete Event: This refers to the follow-up event as defined previously.
For example, to measure the conversion rate from login start to successful login, select Login Process Start and Login Success.
-
-
Use the Event Validation Report to confirm whether the configured events have coverage across the required integrated platforms. Deploy any required uncovered events in Semantic Mapper.
For example, if the Validate Report shows that a selected event for Login Success is missing from the Web platform, use Semantic Mapper to map and deploy that event, so the Login Success metric includes the related activities of Web users.
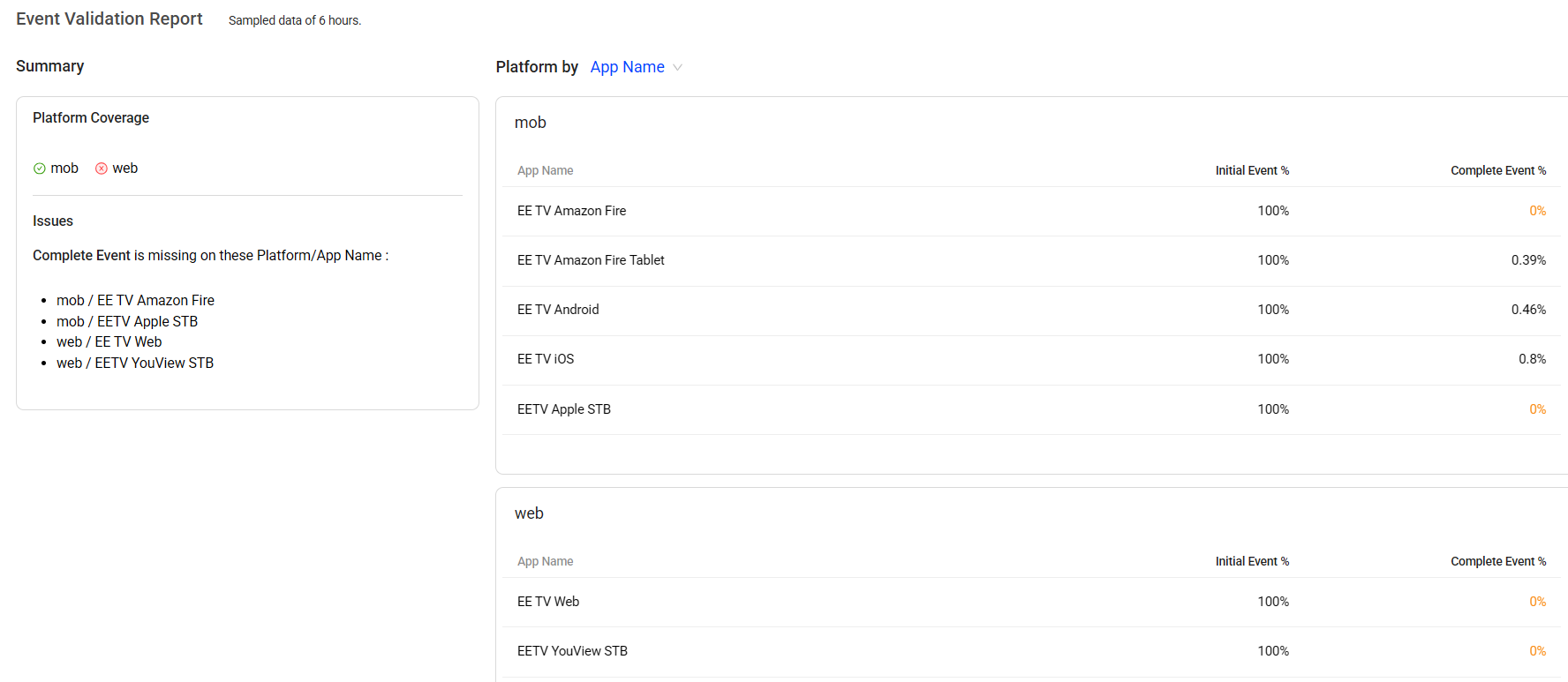
-
Configure metric details:
-
Select the conversion type, Conversion Rate or Conversion Count.
-
Set a criteria for the desired conversion window (or time boundary/constraint) for the paired events’ occurrence per pairing logic for the fields of Calculate Conversion Rate / Conversion Count of successful conversions within a given seconds/minutes/hours.
As the same events can appear multiple times in an app process, pairing logic specifies the first or last sequential instance of the initial and follow-up mapped events across multiple event instances.
-
First-First Pair: Uses the first Initial Event and the first Follow-up Event as a pair.
-
Last-First Pair: Uses the last Initial Event and the first Follow-up Event as a pair.
For example, to set Calculate Conversion Count of successful conversions of First-First pair within 30 seconds and the Initial Event is Login Screen View and the Follow-up Event is Login Success, the criteria is that the two events must occur within 30 seconds to be considered a successful conversion.
-
-
Select an option from the drop-down list to define whether a higher or lower metric value is considered positive. For example, choosing Higher is better indicates that a higher value is desirable, whereas choosing Lower is better indicates that a lower value is desirable.
-
From the Exclusion Event drop-down list, select an event to exclude sessions in which an unwanted event occurs between the starting and ending events.
For example, to measure how often users who provide a valid email successfully complete sign-up without experiencing a Sign-Up Abandoned state, select Sign-Up Abandoned from the list.
-
(Optional) Select one or more dimensions, specify the applicable events, and configure whether the first observed value or last observed value is used as the dimension value.
For example, to analyze a custom metric related to payment based on the first used payment type, select the payment_method dimension recorded on the Network Request event and choose First observed value. After this selection, the payment_method dimension uses the first value observed in the custom metric, enabling dimensional analysis based on this payment type throughout the metric.
 For Duration metrics
For Duration metrics
-
Select events:
-
Initial Event: The first event that triggers a particular process or workflow. It serves as the starting point for measuring and tracking user interactions or system behavior.
-
Complete Event: A complete event that occurs after the Initial Event. It is a continuation or a result of the initial action. The Follow-up Event helps track and measure user engagement or system behavior beyond the initial interaction.
For example, to measure the average duration from login start to successful login, select Login Process Start and Login Success.
-
-
Use the Event Validation Report to confirm whether the configured events have coverage across the required integrated platforms. Deploy any required uncovered events in Semantic Mapper.
For example, if the Validate Report shows that a selected event for Login Success is missing from the Web platform, use Semantic Mapper to map and deploy that event, so the Login Success metric includes the related activities of Web users.

-
Configure metric details:
-
Set pairing logic:
-
Select either of the options:
-
First-First Pair: Uses the first Initial Event and the first Follow-up Event as a pair.
-
Last-First Pair: Uses the last Initial Event and the first Follow-up Event as a pair.
-
-
Choose either first pair or multiple pairs to define count in the same session.
-
first pair: selects only the first pair in a session.
-
multiple pairs: selects all pairs that meet the pairing logic in the same session.
-
 Pairing Logic
Pairing Logic
As the same events can appear multiple times in an app process, pairing logic specifies the first or last sequential instance of the initial and follow-up mapped events across multiple event instances.
For example, suppose there are two mapped events: Login Screen View indicates viewers opening the login page, and Login Success indicates viewers successfully logging into their accounts. In a session, the events are displayed in the following time order: Login Screen View1, Login Screen View2, Login Screen View3, Login Success1, Login Screen View4, Login Success2.
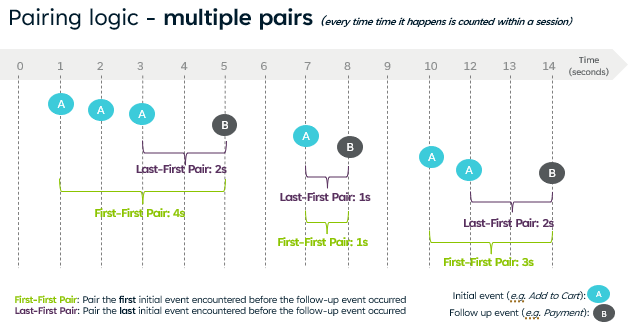
first-first pair last-first pair If selecting first-first pair and first pair If selecting first-first pair and multiple pairs If selecting last-first pair and first pair If selecting last-first pair and multiple pairs Event name Login Screen View1 and Login Success1 Login Screen View3 and Login Success1 Login Screen View1 and Login Success1 Login Screen View1 and Login Success1; Login Screen View4, Login Success2 Login Screen View3 and Login Success1 Login Screen View3 and Login Success1; Login Screen View4, Login Success2 -
-
Set the maximum duration limit.
-
Select an option from the drop-down list to define whether a higher or lower metric value is considered positive. For example, choosing Higher is better indicates that a higher value is desirable, whereas choosing Lower is better indicates that a lower value is desirable.
-
(Optional) To show the distribution of the metric in DPI, select the Distribution check box and fill out the range.
Note: Enabling or disabling the Distribution option for an existing metric does not impact the metric's historical data.
-
(Optional) From the Exclusion Event drop-down list, select an event to exclude sessions in which an unwanted event occurs between the starting and ending events.
For example, to measure how long it takes users who perform a search and receive search results without encountering a Search Error state, select Search Error from the list.
-
(Optional) Select one or more dimensions, specify the applicable events, and configure whether the first observed value or last observed value is used as the dimension value.
For example, to analyze a custom metric related to payment based on the first used payment type, select the payment_method dimension recorded on the Network Request event and choose First observed value. After this selection, the payment_method dimension uses the first value observed in the custom metric, enabling dimensional analysis based on this payment type throughout the metric.
 For Event Aggregation metrics
For Event Aggregation metrics
-
Select the source aggregation event. For example, to measure the total number of application errors, select Application Error.
-
Use the Event Validation Report to confirm whether the configured events have coverage across the required integrated platforms. Deploy any required uncovered events in Semantic Mapper.
For example, if the Validate Report shows that a selected event for Login Success is missing from the Web platform, use Semantic Mapper to map and deploy that event, so the Login Success metric includes the related activities of Web users.

-
Configure metric details:
-
Set the value calculation type. When Total values or Average values are selected, a tag key must be selected from the drop-down list
-
Number: Sets the value to the count of the source events.
-
Total Values: Sets the value to the sum of the event attribute values.
-
Average Values: Sets the value to the average or mean of the event attribute values.
-
-
Select an option from the drop-down list to define whether a higher or lower metric value is considered positive. For example, choosing Higher is better indicates that a higher value is desirable, whereas choosing Lower is better indicates that a lower value is desirable.
-
(Optional) Select the Specify the unit of measurement for the collected data check box, and select the required unit.
-
 For Ratio metrics
For Ratio metrics
-
Set numerator values using one of the options:
-
Select existing aggregation metrics from the drop-down list. For example, to track the revenues per paying user, select the Total Revenue metric that is already created.
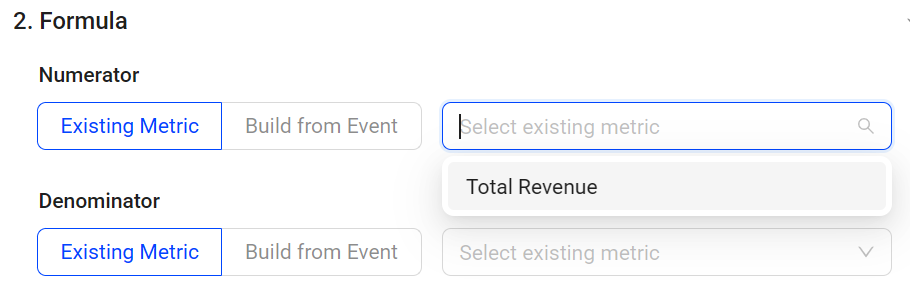
-
Build the metric from an event:
-
Select a target event to measure. Hover over any mapped event to view its detailed mapping rule and efficiently find the appropriate mapped event. For example, to measure revenue, select the mapped event Order_Transaction.
Note: To map a new event for selection, choose an existing mapped event from the drop-down list, clone it, and update the mapping details to create a new mapped event.
-
Specify the calculation, such as counting event occurrences or calculating the total or average values of tags from the selected event. When Total values or Average values are selected, a tag key must be selected from the drop-down list. For example, to measure revenue, select Total values as the calculation method and Revenue as the event tag.
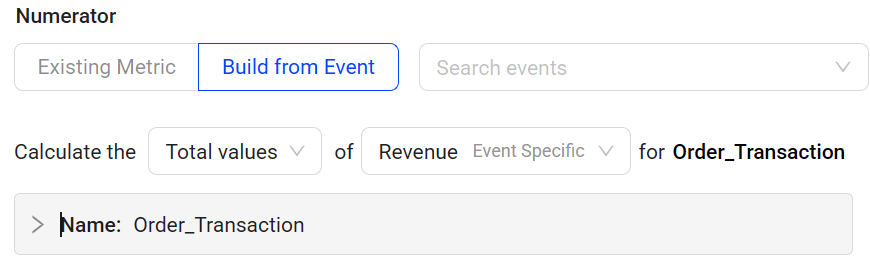
-
Count: Sets the value to the count of source events.
-
Total Values: Sets the value to the sum of event attribute values.
-
Average Values: Sets the value to the average or mean of the event attribute values.
-
-
(Optional) Click Edit to update the event name or event rules.
-
Use the Event Validation Report to confirm whether the configured events have coverage across the required integrated platforms. Deploy any required uncovered events in Semantic Mapper.
For example, if the Validate Report shows that a selected event for Login Success is missing from the Web platform, use Semantic Mapper to map and deploy that event, so the Login Success metric includes the related activities of Web users.

-
-
-
Set denominator values using one of the options:
-
Select existing aggregation metrics from the drop-down list. For example, to track the revenues per paying user, select the Unique Users as the denominator.
When selecting one of these metrics as the Denominator including User Sessions, Unique Users, and Unique Devices, select or clear the check box to control how the denominator is measured based on the analysis objective.
For example, to analyze revenue per paying user, select the check box Only include Unique Users who qualify for the numerator to ensure that only users who actually made a purchase are counted. To analyze revenue per user, clear the check box to include all users in the calculation.
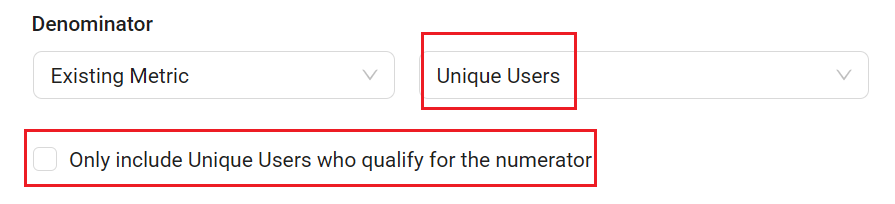
-
Build the metric from an event:
-
Select a source aggregation event. Hover over any mapped event to view its detailed mapping rule and efficiently find the appropriate mapped event.
Note: To map a new event for selection, choose an existing mapped event from the drop-down list, clone it, and update the mapping details to create a new mapped event.
-
Specify the calculation, such as counting event occurrences or calculating the total or average values of tags from the selected event. When Total values or Average values are selected, a tag key must be selected from the drop-down list.
-
Count: Sets the value to the count of source events.
-
Total Values: Sets the value to the sum of event attribute values.
-
Average Values: Sets the value to the average or mean of the event attribute values.
-
-
(Optional) Click Edit to update the event name or event rules.
-
Use the Event Validation Report to confirm whether the configured events have coverage across the required integrated platforms. Deploy any required uncovered events in Semantic Mapper.
For example, if the Validate Report shows that a selected event for Login Success is missing from the Web platform, use Semantic Mapper to map and deploy that event, so the Login Success metric includes the related activities of Web users.

-
-
Use a fixed number as a denominator:
Select Fixed Number from the drop-down list and enter the desired value in the field. For example, when analyzing revenue in euros based on U.S. dollar data, apply the current USD-to-EUR exchange rate as the fixed denominator to calculate the Ratio metric for a common currency analysis.
-
-
Configure metric details:
-
(Optional) Select the required unit from the drop-down list.
-
Select an option from the drop-down list to define whether a higher or lower metric value is considered positive. Choosing Higher is better indicates that a higher value is desirable, whereas choosing Lower is better indicates that a lower value is desirable. For example, to track the revenues per paying user, select Higher is better.
-
-
-
Click Save and Deploy to complete the deployment.
Note: When updating custom metrics, use the Keep historical data checkbox to control whether existing data is retained. Select the checkbox to keep the data, or clear it to remove it. The checkbox is selected by default.
The deployment takes several minutes to take effect.
User Flows can be configured to capture user outcomes of a specific task within an application, such as login, search, and checkout. The Flows feature provides a preset dashboard to quantify business KPIs using predefined metrics, such as success rate, duration, inits, and errors, including conversions with errors.
Furthermore, Flows enable different teams, typically restricted to siloed data, to share the same performance data context, connecting business KPIs, user app experiences, and service performance for comprehensive cross-functional analysis.
Flow metadata enables efficient troubleshooting and root cause analysis by capturing flow-specific dimensions, such as:
-
Business-specific dimensions: For example, credit card type in a payment flow. These are not part of global metadata but are highly relevant to the specific flow.
-
Error dimensions: Error reason, error message, and error ID.
-
Network request dimensions: Endpoint, host, path, and response code.
After creating flows, the corresponding metrics are created automatically.
 Flow Metrics
Flow Metrics
| Metric | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Flow Name Init (Use the first initial event) |
The number of initial events within the user-defined Flow Duration Limit, maximum 1 hour. Count the First initial event if multiple initial events happen (user configured). |
|
Flow Name Init (Use the last initial event) |
The number of initial events within the user-defined Flow Duration Limit, maximum 1 hour. Count the Last initial event if multiple initial events happen (user configured). |
|
Flow Name Complete # % |
Complete #: The number of initial events followed by a complete event within the user-defined Flow Duration Limit , maximum 1 hour. Complete %: Complete # / Init |
|
Flow Name Avg Complete Duration |
The average time from the initial event to the complete event within the user-defined Flow Duration limit, maximum 1 hour. |
|
Flow Name Success # % |
Success #: The number of completed flows (initial event followed by a complete event within the configured success window). Success %: Success # / Init |
|
Flow Name Flows with Errors # % |
Flows with Errors #:The number of Flows with at least one error. Flows with Errors %: The number of Flows with errors divided by the total number of Flows. |
|
Flow Name Abandoned Flows # % |
Abandoned Flows #: Initial events with no complete event or with a complete event occurring beyond the user-defined Flow Duration Limit (up to 1 hour). Abandoned Flows %: Abandoned Flow # / Init |
|
Flow Name Abandoned Flows with Errors # % |
Abandoned Flows with Errors #:The number of abandoned flows that had at least one error. Abandoned Flows with Errors %: Abandoned Flows with Errors # / Init |
|
Flow Name Completed Flows with Errors # % |
Completed Flows with Errors #: The number of completed Flows with at least one error. Completed Flows with Errors %: Completed Flows with Errors # / Init |
|
Flow Name Total Error Count |
The total number of Flow errors in both completed and abandoned flows. |
|
Flow Name Errors in Abandoned Flows |
The number of errors in abandoned Flows. |
|
Flow Name Errors in Completed Flows |
The number of errors in completed Flows. |
|
Flow Name Network Request Avg Duration |
The average network request response time after the first initial event within the Flow completion window, maximum 1 hour. |
|
Flow Name Network Request Failure # % |
Network Request Failure #: The number of network request failures on or after the first initial event within the Flow completion window, maximum 1 hour. Network Request Failure %: Network Request Failure # / Network Request Count |
|
Flow Name Network Request Count |
The number of network requests on or after the first initial event within the Flow completion window, maximum 1 hour. |
Follow these steps to create flows.
 Create Flows
Create Flows
-
Start with the location:
-
Activation Home Page
-
Metric Builder
-
Flow Widget in Trends
-
-
Enter the flow name, description, and labels.
-
Flow name. For example, to track the journey starting from clicking the play button and ending with successful video playback, enter 'Initiate video playback'.
-
(Optional) Flow description. For example, enter ‘User clicked the play button and successfully started playing a video.’ This flow represents the explicit user action to begin video consumption from a control element.
-
(Optional) Labels. Enter Flow labels to clarify the Flow use in the UI. For example, enter Payment to label Flows related to the payment process, such as the Flow from login to payment. Flows with labels are grouped by labels in the Overview dashboard.
For existing labels, click the kebab menu to edit or delete them.
-
-
Identify which events to select:
 Check Predefined Events
Check Predefined Events
Predefined events include Conviva predefined events and events that are already mapped. Creating custom metrics based on these predefined events can often save time.
Check the predefined events from the drop-down list for event selection. For example, to track the journey starting from search and ending with video playback, review the predefined events in the drop-down list. Look for events that indicate the a search button click and a video play button click.
Note: To update predefined events, clone them first, then configure the tag keys and values.
 Discover New Events with EventLooker and LiveLens
Discover New Events with EventLooker and LiveLens
In most cases, predefined events may not fully meet metric creation requirements. Map the required events and create metrics based on the newly mapped events.
Use the tools to check raw events and map the events for requirement:
-
EventLooker: Allows browsing and searching events and tag keys. Use the drop-down list to apply a selected event.

-
LiveLens: Provides real-time event names and tags while interacting with an application. To learn how to use LiveLens, see LiveLens.
-
-
Select events that signal the start and end of a user flow.
-
Initial Event: signals the start of the user flow in the app.
It is usually a user interaction in the app (such as a search button click or a page view indicating that users exposed to the search page).
Note: When a network request is set as an initial event in a Flow and the Flow complete event occurs very close to the initial event, such as within seconds, the Flow conversion data may be impacted.
-
Complete Event: signals the positive outcome of a user flow in the app.
For example, a Page View of Payment Acknowledgement Page or Network Requests with response code indicating payment success
-
-
Use the Event Validation Report to confirm whether the configured Flow events have coverage across the required integrated platforms. Deploy any required uncovered events in Semantic Mapper.
For example, if the Validate Report shows that a selected Flow complete event for Login Success is missing from the Web platform, use Semantic Mapper to map and deploy that event, so the Login Flows metrics include the related activities of Web users.

-
(Optional) Set experience and performance settings.
-
Error Event: includes errors that matter in the defined flow.
Select error events from the drop-down list, or add them using the Event Looker Tool.
Conviva presets default errors, such as "5xx server error" and "app crash", enabling a breakdown of total errors by each error event in the Flow Preset dashboard.
To make error analysis more actionable, include custom error events that capture login-specific errors such as login errors during the login flow.
-
Network Request: associates the network request with a flow.
Click +Add Network Request, define the list of Host and Path that representing service and APIs running underneath the flow. The system only consider the network requests that match these rules in the metrics including Network Request Avg Duration, Network Request Failure, and Network Request Count.
Note: Based on above association, below metrics and dimensions are available in Flow preset dashboard.
Dimensions: Network Request Endpoint, HTTP Method, Response Code, URL Host, and URL Path
Metrics: Network Request Avg Duration, Network Request Failure, and Network Request Count
-
-
Configure Flow Widget, such as time constraint and distribution range.
-
Set the success time boundary which determines flow success.
For example, setting the login flow success to completion within 90 seconds, labels any flows that exceed 90 seconds unsuccessful.
-
Set the Flow duration limit.
For example, setting the custom metric duration limit to 60 seconds excludes any app sessions with durations that exceed the 60 second limit from the metrics.
-
Set the percentage thresholds to determine whether the success rate is considered Good or Poor.
Note: Success rate is calculated by dividing the total number of successes (initial events followed by a complete event within the defined time boundary) by the total number of initial events.
-
Define the expected value range for durations to display on the distribution chart. Toggle to distribution chart from the metric card Avg Duration in the Flow preset dashboard.
By default, DPI sets the maximum value to double the success time boundary, with the option to manually adjust the range. For example, setting the range to 0–120 seconds displays 40 bars representing the distribution of durations for each completion.
For example, to visualize acceptable user interaction times, set the duration range from 20 seconds to 200 seconds.
-
(Optional) From the Exclusion Event drop-down list, select an event to exclude sessions in which an unwanted event occurs between the starting and ending events.
For example, to measure how often returning users who provide a valid email and advance from the Email screen to either the Password page or the Account Recovery page without experiencing a Sign-Up reroute state, select sign-up from the list.
-
(Optional) Select one or more dimensions, specify the applicable events, and configure whether the first observed value or last observed value is used as the dimension value.
For example, to analyze payment Flow based on the first used payment type, select the payment_method dimension recorded on the Network Request event and choose First observed value. After this selection, the payment_method dimension uses the first value observed in the Flow, enabling dimensional analysis based on this payment type throughout the Flow.
-
-
Click Save and DPI creates the corresponding metrics automatically. For the flow metric details, see Flow Metrics.
Note: When updating flows, use the Keep historical data checkbox to control whether existing data is retained. Select the checkbox to keep the data, or clear it to remove it. The checkbox is selected by default.
Conviva supports associating predefined dimensions (Element Classes, Element Id, Element Name, Element Text, and Element Type) with Flow metrics, enabling drill-down analysis for Flow metrics. Conviva also automatically associates the related network request dimensions (Network Request Url Host, Network Request Http Method, Network Request Url Path, Network Request Response Code) with Flow metrics, excluding the Flow error metrics, to enhance the analysis of Flow performance. -
Click Deploy to use the metrics for analysis on the Trends dashboard.
For example, after deploying the metrics based on the 'search for playing videos' flow, go to the Trends dashboard to review the metrics and identify key insights for optimizing application performance and improving the user experience. An increase in the duration between the initial and complete events indicates slower performance while a decrease in success % indicates issues or blockers to user journey completion within the time constraint.
Note: A flow can span multiple sessions as long as the time between sessions does not exceed the 5-minute inactivity timeout window and the overall duration is within the 1-hour flow completion window.
The Semantic Mapper tab provides functionality to map raw events to clearly identifiable user behaviors , block unnecessary events from the sensor, create custom dimensions with values extracted from events, and semanticize page/screen titles.
For example, map raw events using tag key/values, such as the screen_view raw event with tag key screen_name and tag value login_page, to build meaningful specific events for metric creation, and create custom dimensions to track user types or device categories.
The Semantic Mapper also leverages backend-driven event management and remote mapping to enable event mapping and updates with minimal front-end effort.
 Map New Events
Map New Events
This option provides a comprehensive mapping process that enables step-by-step definition and configuration of semantic events.
Explore the Events
The Semantic Mapper page allows the viewing of common events and exploring which events require mapping. To optimize event management, Semantic Mapper displays only high-volume events. Other less frequent events can be mapped manually.
Note: If the required events and their corresponding tag keys and values are already known, the exploration process can be skipped.
-
To access the Semantic Mapper page, from the DPI application, select Activation.
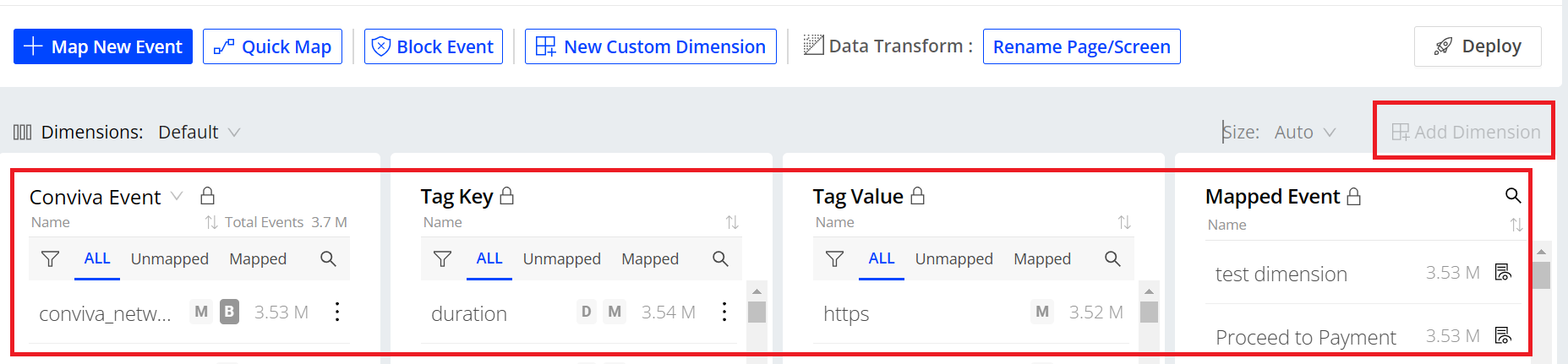
Under the Semantic Mapper tab, drop down lists display on the page and allow the viewing of all events, event tag keys, event tag values, and mapped events. Click Add Dimension to add dimension drop down list to help explore events.
-
To view the unmapped events in the specific time range, in the time range bar, select the desired time range, such as May 24 to May 26.
-
Check the unmapped events and confirm which unmapped event requires mapping based on these points:
-
Consolidate event names to simplify event recognition.
-
Group related events to optimize event presentation and correlate app activities.
-
-
Confirm the event tag key and event tag value for the event which will be mapped.
-
To filter all data related with the event, from the dimensional list, click the event. For example, double click screen_view.
-
From the drop-down list, select Event Tag Key, and then click the specific item of tag key. For example, to map screen_view to a clear event that shows which kind of screen viewers viewed. Click screen_name.
-
From the drop-down list, select Event Tag Value to view all the tag values of the event tag key, and confirm the event tag values.
For example, for the event screen_view with the screen_name tag key, the event tag values are login_welcome, login_username, login_link, and so on. To use a single mapped event that indicates viewers viewed login screen, the event tag values is login_welcome.
-
For example, the event screen_view does not indicate which kind of screen viewers viewed. Map the event with the tag key screen_name and the tag value login_welcome to Login Screen View. This mapping assists in clearly identifying and analyzing a viewer behavior when the viewer views the login screen. This mapping assists in clearly identifying and analyzing a viewer behavior when the viewer views the login screen.
When using Semantic Mapper to map events displayed in LiveLens, keep in mind that some event tag keys names may have slight variations as shown below.
|
Predefined Tag Key Name in LiveLens |
Tag Key Name in Semantic Mapper |
|---|---|
| Button Click Element Text | buttonClickText |
| Button Text | conviva_button_click / elementText |
| Duration | requestDuration / duration |
| Screen Title | pageTitleAndScreen / conviva_screen_view |
| Page Url | pageUrl |
| Page Title | pageTitle / conviva_page_view / page_title |
| Link Click Element Target | linkClickTarget |
| Link Target | conviva_link_click |
| Target Url | requestTargetUrl / targetUrl |
| Previous Screen Title | previousScreen |
| Network Request Response Code | requestResponseCode / responseStatusCode |
Note: When using requestSize as a tag key, note that the request size is determined by the Content-Length header in the HTTP request, which defines the size of the HTTP body.
Set Mapping Rules and Deploy Mapped Events
After confirming the event that needs to be mapped, and the related event tag key and event tag value, set mapping rules for mapping events.
-
To access the page, click +Map New Event from the main page.
-
Fill up the fields in Set Mapping Rules by using one of the options:
Note: If the event rule matches an existing one, a reminder message appears. Click Yes to apply the duplicate rule to the new event mapping. Click No to cancel the mapping.
-
If there are previously explored events using the mentioned steps, click Map This to set the rules automatically.
When setting the tag value, there are several conditions and rule options available, such as "contains", "not contains", "equals", "not equals", "is empty", "is not empty", "starts with", and "ends with", as well as "or" and "and" rules.
Note: Is not empty: Indicates the string contains at least one character. Is empty: Includes cases where the string is either empty (contains zero characters) or null (has no value).
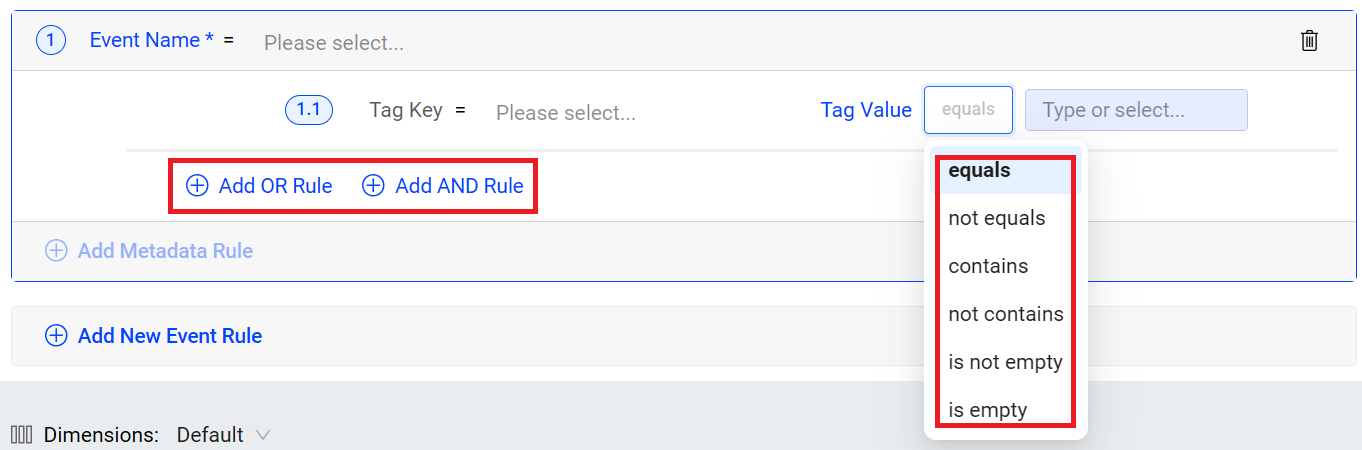
Example:
For the event _user.login with the event_action tag key, the event tag values are Success and success. To have a mapped event that indicates the success login, use one of the options.
-
Option A: Set the tag Value to contain uccess.
-
Option B: Set a tag value to equal Success, click “Add OR Rule” and then set the tag value to equal success.
-
-
If there is a clear understanding of the events that need to be mapped and the corresponding tag key and tag value, follow the step:
-
From the drop-down list of Event Name, Tag Key and Tag Value, select the event name, tag key and tag value, or fill them out directly. For example, select screen_view, screen_name, and login_welcome.
Note: Use multiple conditions and rule options at the disposal when configuring the tag value. Refer to the previous note for further details.
-
-
-
Select a suitable category and type the event name in the Set Mapped Event field. For example, use Login Screen View as the mapped name and select Login/Logout.
-
Click Save.
-
On the Semantic Mapper page, click Deploy, select the specific items on the Deployment Confirmation page, and click Deploy.
-
After deploying, check the total number of the mapped events on the Semantic Mapper page and also use the mapped events as dimension values on the Trends page.
Note: Conviva DPI applies event mappings to only newly initiated sessions. Updates to on-going sessions and sessions that restart within the 5-minute inactivity period appear after the next session starts.
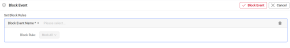
 Block Event
Block Event
DPI enables intelligent data collection to block the reporting of irrelevant or meaningless events from the sensor, ensuring the accuracy and relevancy of data.
-
To access the Block Event page, click Block Event from the main page.
-
On the “Set Block Rules” section, from the “Block Event Name” drop-down list, select the event that needs to be blocked. For example, choose conviva_network_request.
-
To set block rules, choose one of the options based on the requirements.
-
To block all the events selected in step 2, select Block All.
-
To block the specific events that are based on the events selected in step 2, select Block if…, and fill out the key values that the specific event owns. Add multiple block rules for different specific events by clicking Add OR Rule.
For example, to block the conviva_network_request event that triggered when loading images, select Block if…, and fill out the key values as .png, .jepg, and .jpg.
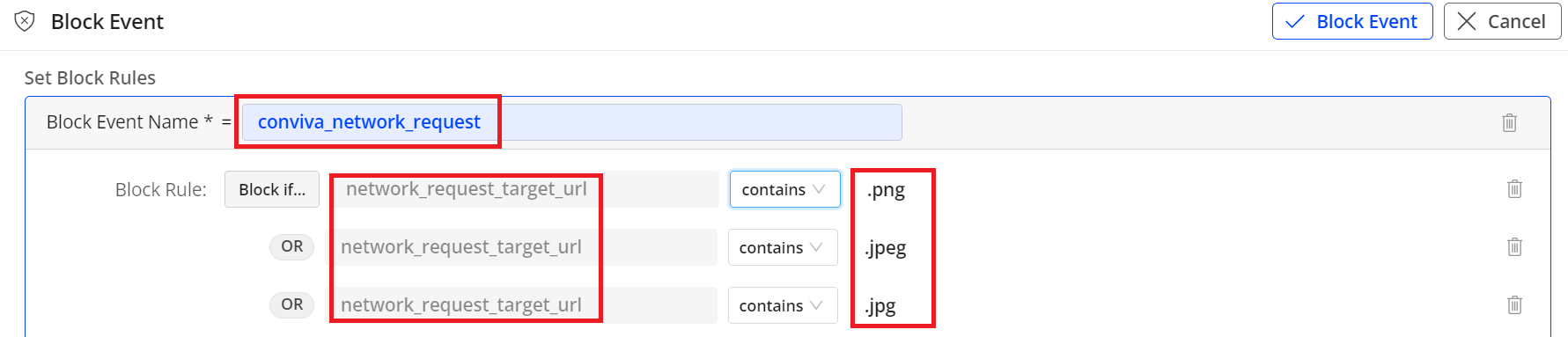
-
-
To apply the block rules, click Block Event from the top right corner.
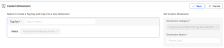
 Create Custom Dimensions
Create Custom Dimensions
Custom dimensions are extracted from event keys to provide enhanced levels of dimensional analysis in Trends dimension tables and AI alerts. With custom dimensions, analyze application performance and user behaviors more efficiently and flexibly.
Create custom dimensions with values extracted from events to enhance analysis of application performance and user behaviors, such as a dimension value extracted from only the play start and play end events.
Manage custom dimensions along with events in the Management page.
For example, create a custom dimension based on the Player Name event tag key and select mapped events to determine the dimension values. This new dimension enable the analysis of application player performance across different player dimensions in the Trends dashboard.
-
Click New Custom Dimension.
-
Select a tag key from the drop-down list or enter it directly.
The label next to the tag key indicates how it is collected:
-
Event-Specific Tag: The tag is only reported by certain events.
-
Global Tag: The tag is reported on all events as part of the global context.
Note: If the entered tag key is not in the drop-down list, after entering it, select the event type which is either global or event-specific.
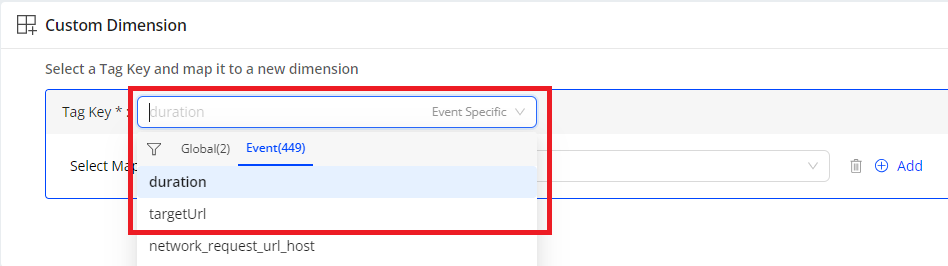
Note: When creating a custom dimension and entering a tag key name, the Tag Key list displays up to 500 matching tag keys. If the desired tag key is not listed, locate it in the Tag Key table, click the kebab icon next to the tag key name, and select New Custom Dimension to add the tag key to the Tag Key field in the Custom Dimension area. Alternatively, use the global filter in the Semantic Mapper to find the tag key in the Tag Key table.
-
-
Configure tag keys based on tag type.
Global Tags:
For persistent tag keys, select the tag key collected as global context to treat the tag as a global dimension.
Note: No event scoping is required. The dimension is automatically computed across all relevant traffic.
Event-Specific Tags
For tag keys collected only on specific events:
-
Select All applicable events to compute the custom dimension value using every event that reports the tag key.
-
Select Specific Mapped Event to compute the custom dimension value using only explicitly selected mapped events.
Note: Selecting a broader event scope increases the volume of computation and may impact cost.
Advanced Option: Promote Event Tag as Global Dimension
For event-specific tag keys, enable Promote as Global Dimension to treat the tag as a global dimension.
When enabling this option:
-
The tag key is treated as a global dimension for all incoming traffic going forward.
-
The dimension value is derived from the earliest occurrence within a session.
-
After setting the tag key as a global dimension, the value remains the same for the duration of the session and does not update until:
-
A new session starts, or
-
A new flow record begins.
For example, the AccountStatus tag key is reported on account-related events. After enabling Promote as Global Dimension, the system treats AccountStatus as a global dimension and enables analysis of all related events within the session as dimension values, such as page views, clicks, and purchases, based on the account status value including upsell, silverPlan, and goldPlan, captured at the earliest point in the session.

Note: Promotion applies only to future data and does not retroactively update historical records.
-
-
-
In the Set Custom Dimension field, set the dimension name.
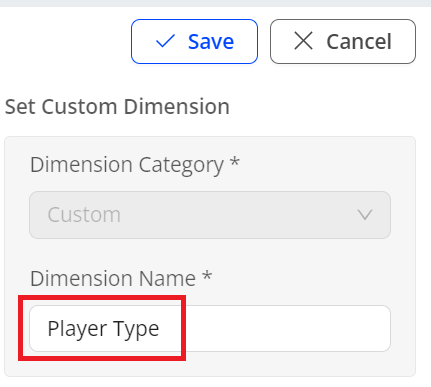
-
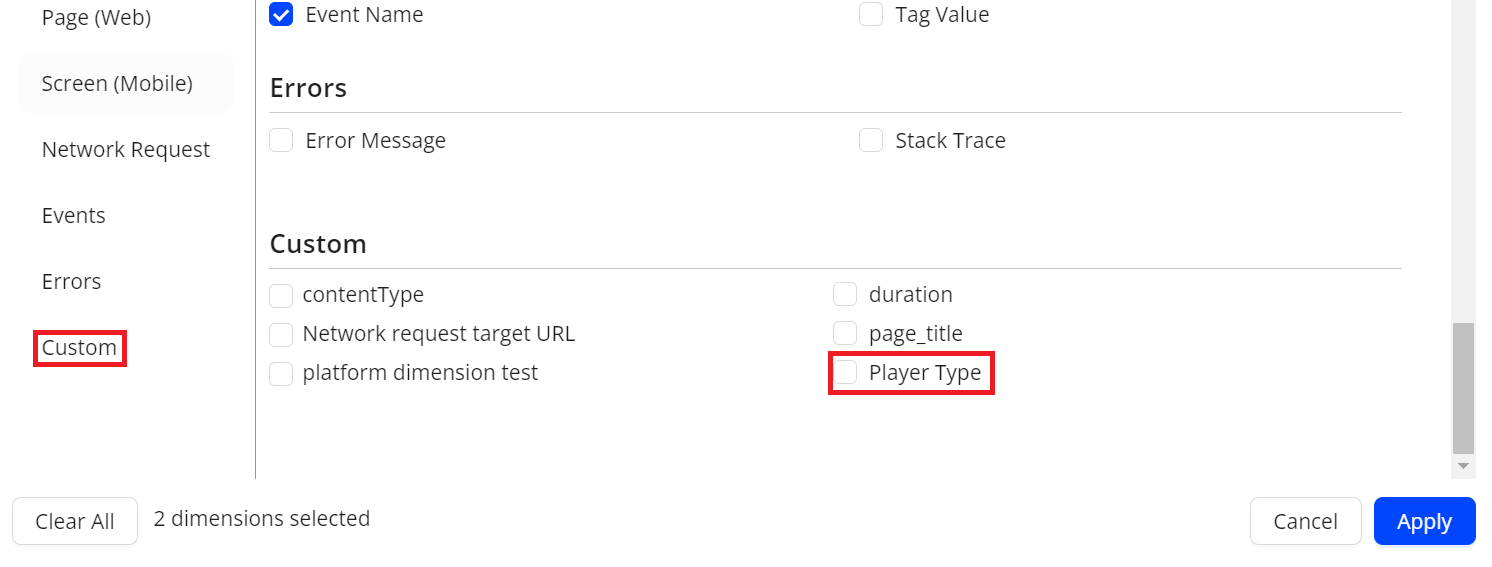
In the Trends dashboard, click + Dimension from the Dimension table, and check whether the created dimension is in the Custom list. Select the check box to apply the new dimension to the dimension tables.
-
(Optional) To edit a custom dimension, choose either:
-
Go to the Management tab, edit the custom dimension from the Custom Dimension table. For more information, check Management.
-
Go to the Semantic Mapper tab, select the desired custom dimension from the dimension drop-down list, click edit, and make necessary updates.
-
The Management tab allows the effective data management such as metrics and events, including tasks for searching, reviewing, deleting, and deploying/undeploying to support performance monitoring goals. The tab also allows multiple selections of metrics, custom dimensions, and mapped events for deployment, undeployment, and deletion. Click Download for exporting Management data in xlsx format, enabling easier auditing of Activate changes.

 Metrics
Metrics
Custom metrics are created based on mapped events. With custom metrics, analyze application performance and user behaviors more efficiently and flexibly.
The Metrics tab provides easy access to review created custom metrics and associated details such as status, mapped events, and user updates.
Searching Custom Metrics
To quickly find a custom metric, enter a portion of its name. For a more refined search, select the Show Filters check box and select the filter conditions to match the desired metrics.
 Mapped Events
Mapped Events
Use the Mapped Events table to easily review the current mapped events names and associated details such as status, category, and related metrics. Perform various management actions to optimize the mapped events, such as undeploying and deleting unused events.
Searching Mapped Events
-
To quickly locate a mapped event, simply enter part of its name.
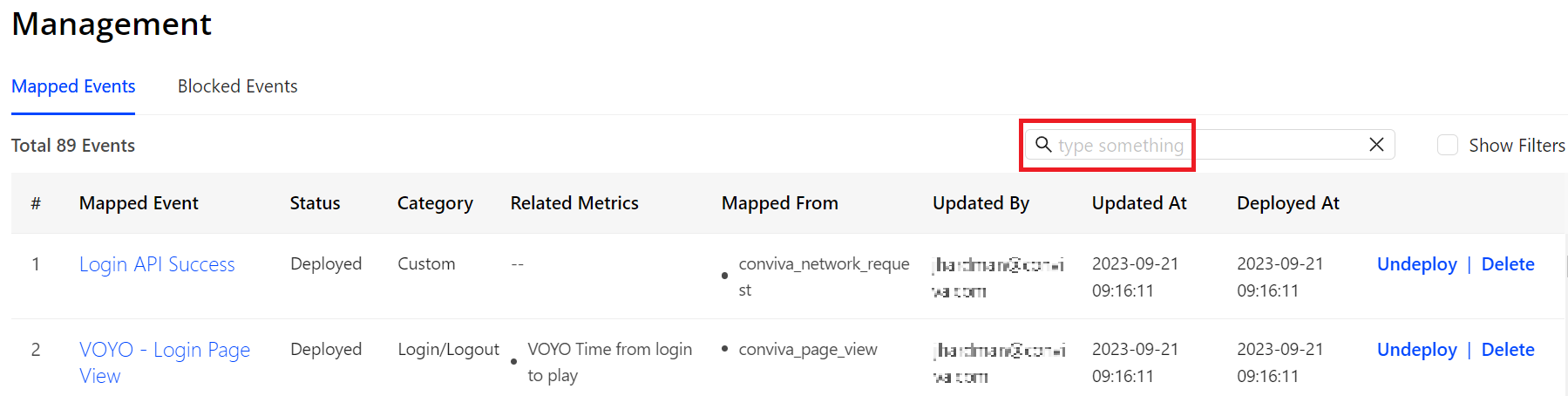
-
For a more refined search, select the Show Filters check box and select the filter conditions to match the desired events.
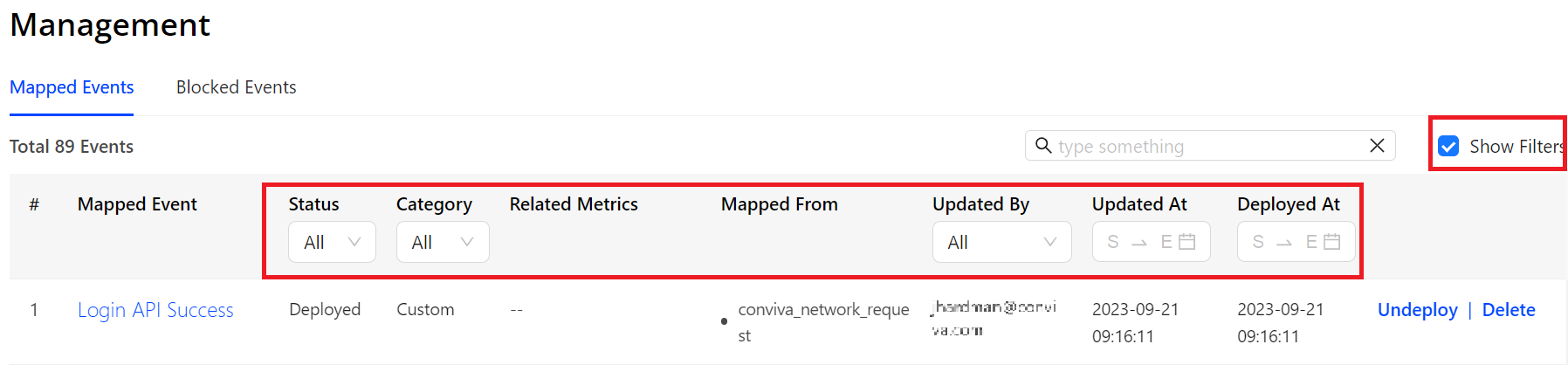
Editing Mapped Events
If the mapped event is unsuitable, directly update the mapped event in the Management tab.
-
Find the mapped event that needs to be modified and click its name.
-
The pop-up window displays event details. Click Edit, edit the event, such as the name, category, and mapping rules, and click Save Changes.
 Custom Dimension
Custom Dimension
Custom dimensions are extracted from event keys to provide enhanced levels of dimensional analaysis in Trends dimension tables and AI alerts. With custom dimensions, analyze application performance and user behaviors more efficiently and flexibly.
With the Custom Dimension , easily review created custom dimensions and associated details such as status, mapped tag keys, and updates made by users. Perform various management actions such as deploying or undeploying each dimension, as well as editing and deleting these dimensions. Create custom dimensions using Semantic Mapper.
Note: Deleting a dimension that is already used in dashboards or filters results in the dimension becoming unavailable for further use. Additionally, pop-up messages appear in dashboards and filters after deletion.
Searching Custom Dimensions
To quickly find a custom dimension, enter a portion of its name.
Editing Custom Dimensions
To make updates to a custom dimension, such as modifying its name or tag key:
-
Locate the custom dimension that needs to be edited.
-
To access the pop-up window for editing, click the custom dimension name.
-
In the pop-up window, click Edit, make the necessary changes, and click Save Changes.
 Cloning Metrics, Dimensions, and Events
Cloning Metrics, Dimensions, and Events
To simplify the process of creating metrics, dimensions, and events similar to existing ones, start with a clone of an existing settings and modify only the required changes.
-
Click the Clone icon in:
-
Tables for the Metrics, Custom Dimensions, and Mapped Events in the Activation dashboard Management tab
-
Metric, Custom Dimension, or Mapped Event Details pages
-
-
Click Save to apply the updates.
LiveLens helps find accurate event names and tags in real time while using the application, supporting preparation for event mapping and metrics building.
For example, raw events occurring during a web application login, such as authentication API calls, login button clicks, or success tokens, can be identified as critical login process milestones. Using the Semantic Mapper, these raw events can then be mapped to create metrics monitoring the login process duration.
Note: The User dashboard provides a historical record of mapped events to track past user behaviors and event sequences.
 Exploring Events in Real Time
Exploring Events in Real Time
With the LiveLens, efficiently explore application events that occurred to monitor the event flows (initial and follow up events) that can be used to create the most meaningful and actionable metrics.
Note: After opening the LiveLens, data from the past 5 minutes displays and new data continues to be appended from the time when opening the LiveLens.
-
From the DPI menu, click Activation, then click the LiveLens tab on the Activation page to access the LiveLens page.
-
Locate the device running the application in which events will be monitored.
Note: By default, the Find Myself By IP Address option and the current IP address are automatically selected.
Select one of the options based on the requirements:
-
Find Myself By IP Address: If the DPI application and the device running the application are on the same network, the current IP address is automatically fetched by LiveLens. If not, enter the IP address that the device is using. Use the search engine on the device to find the IP address.
-
Find Myself By User ID: Use the user account ID to locate the device.
-
Find Myself By Client ID: Use the client ID to locate the device.
-
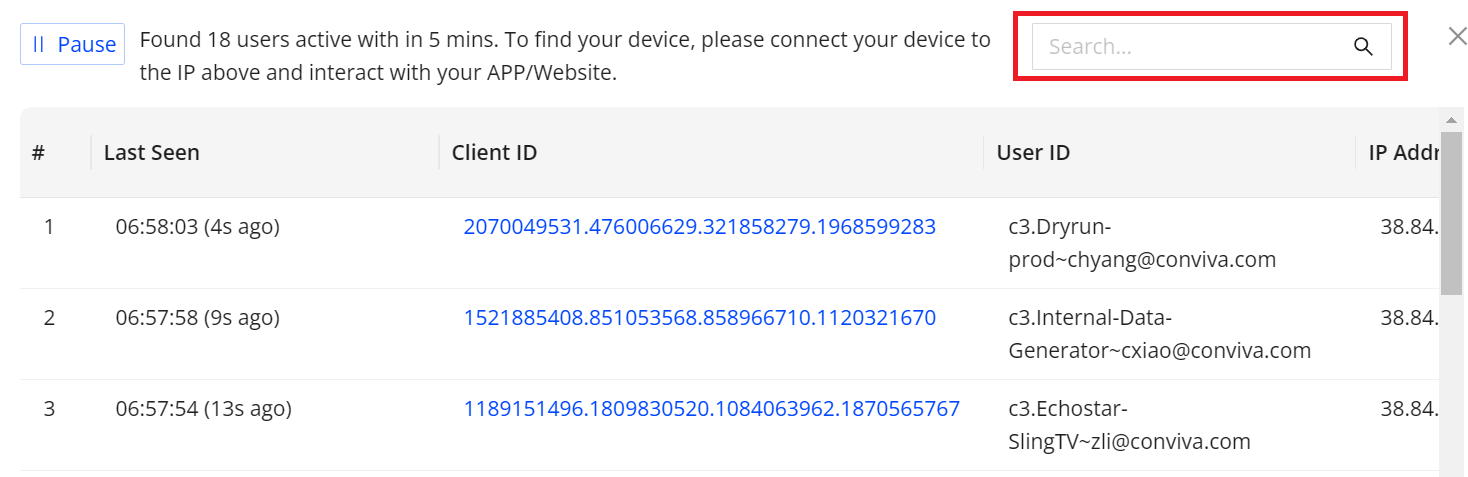
-
Locate the active user from the pop-up table and click the client ID to open the Real-time Timeline area for that user. Use the search function to find the required user through user ID matching.
-
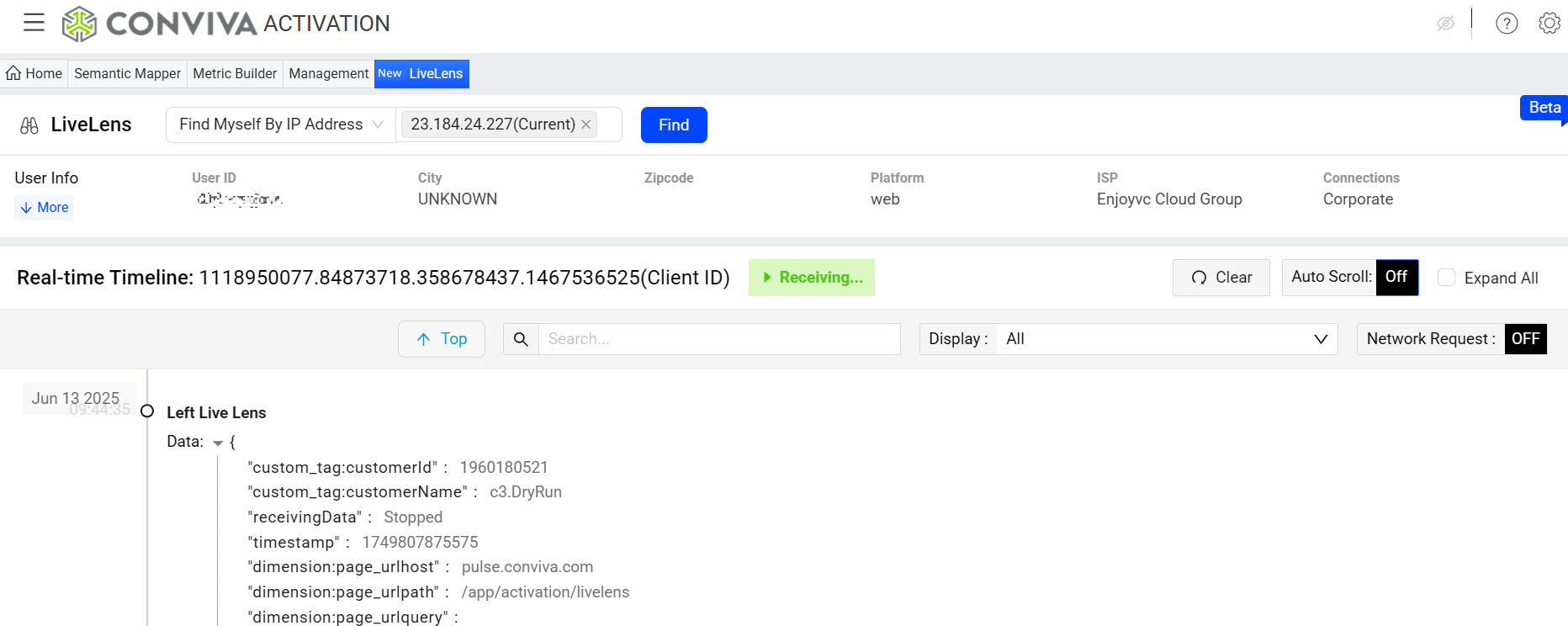
Explore the events in the Real-time Timeline area.
For example, all the raw events related to the user activities that occurred within 5 minutes after clicking the login button.
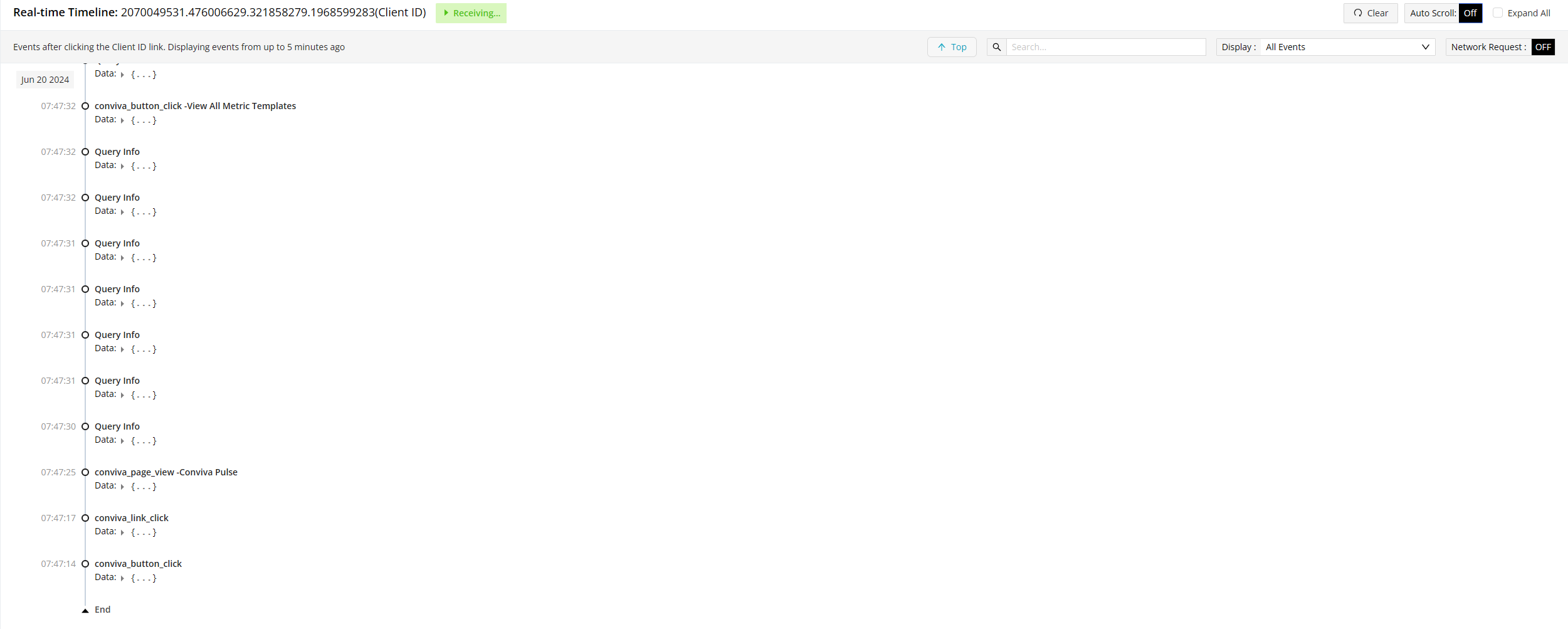
Click the Data Expander to display the data details. The details are useful for mapping events. For example, use the conviva_button_click data to determine elememtID: menu-toggle, and elementType:submit. Map the conviva_button_click raw event, by using elementID or elementType as a tag key and menu-toggle or submit as the corresponding tag value.
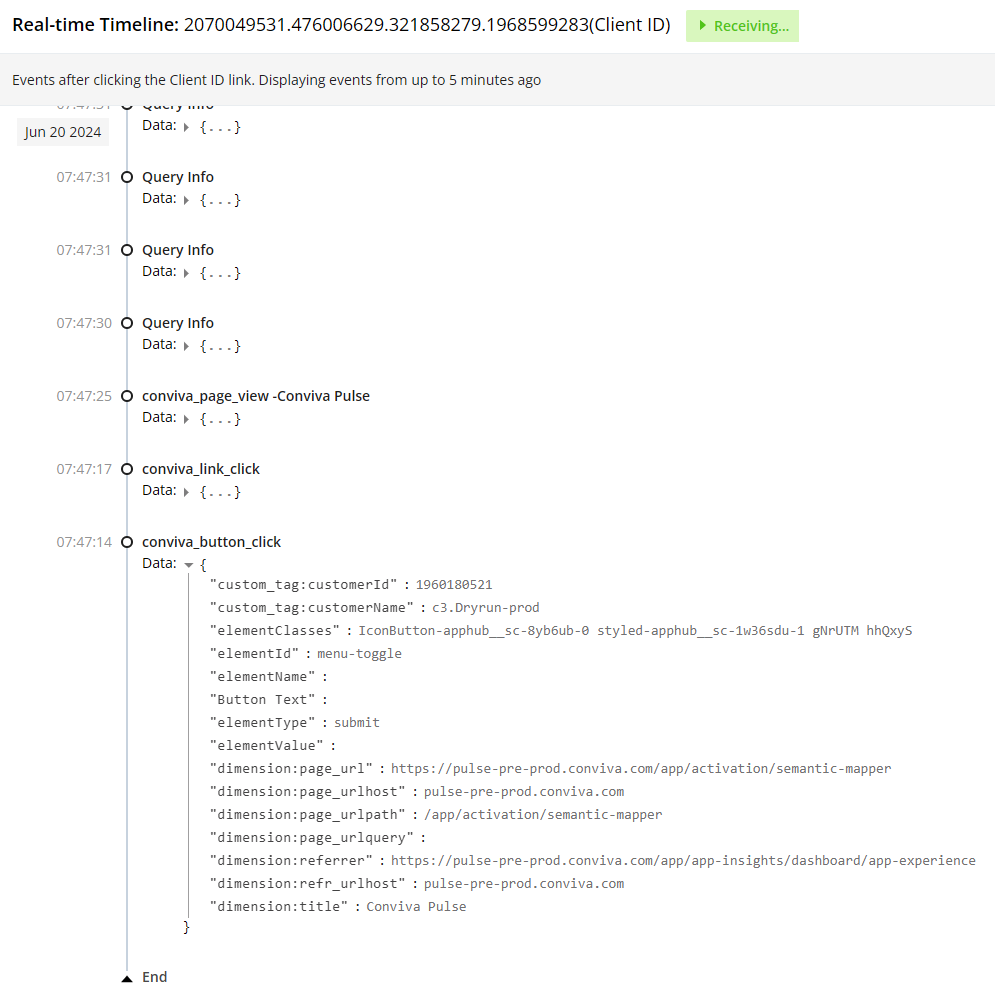
When using Semantic Mapper to map events displayed in LiveLens, keep in mind that some event tag keys names may have slight variations as shown below.
Predefined Tag Key Name in LiveLens
Tag Key Name in Semantic Mapper
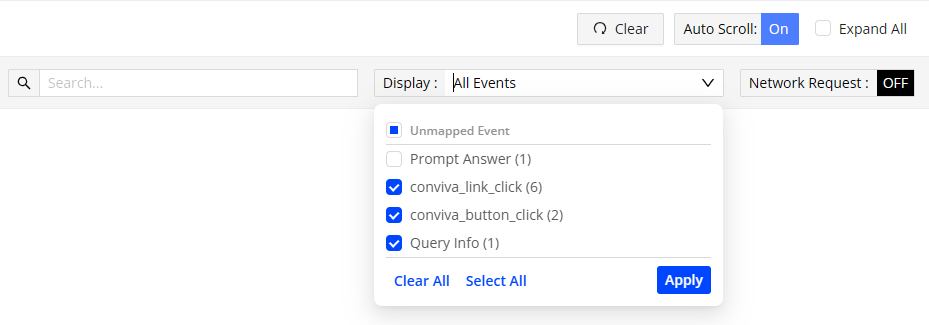
Button Click Element Text buttonClickText Button Text conviva_button_click / elementText Duration requestDuration / duration Screen Title pageTitleAndScreen / conviva_screen_view Page Url pageUrl Page Title pageTitle / conviva_page_view / page_title Link Click Element Target linkClickTarget Link Target conviva_link_click Target Url requestTargetUrl / targetUrl Previous Screen Title previousScreen Network Request Response Code requestResponseCode / responseStatusCode Additional functions for efficient event exploration include:
-
Clear button: Clears all displayed raw events and starts showing new events that occur after clicking the Clear button.
-
Auto Scroll: Enables automatic scrolling of the data for raw events, so the displayed events refresh without user intervention.
-
Expand all: Selects the check box to display all data for raw events.
-
Search box: Allows input of keywords to quickly locate matching raw events.
-
Display: The drop-down list shows all raw events grouped by raw event names, with options to clear and select specific events.
-
Network Request: Enables or disables the display of events related to network requests. By default, this option is disabled.
-
The Sensor Remote Control allows post-integration configuration of the DPI sensors to collect, block, or enable/disable data ingestion according to the business needs.
Note: Conviva strongly recommends updating the sensor to its latest version, which is more powerful with advanced features.
By default, the Blocked Events section is displayed.
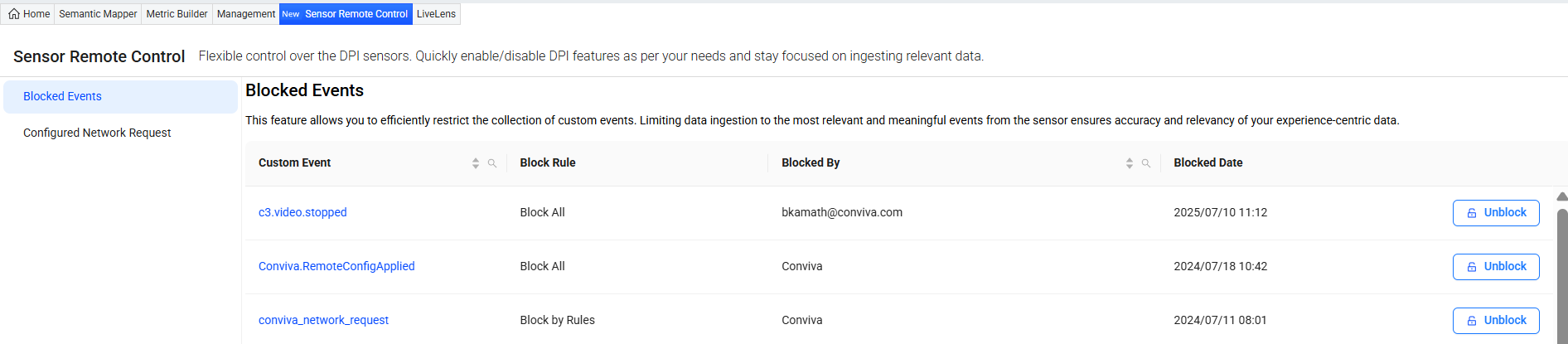
 Blocked Events
Blocked Events
Block event allows preventing irrelevant or meaningless events to get collected from the sensor, ensuring the accuracy and relevancy of data ingestion. The Blocked Events list shows the events that are blocked along with the block rule, blocked by user, and blocked date. Use this section to perform various actions such as, searching, modifying, and unblocking the blocked events.

Searching Blocked Events
-
To find a blocked event, click the search icon adjacent to the Custom Event column, enter part of the event's name in the search window, and click Search.
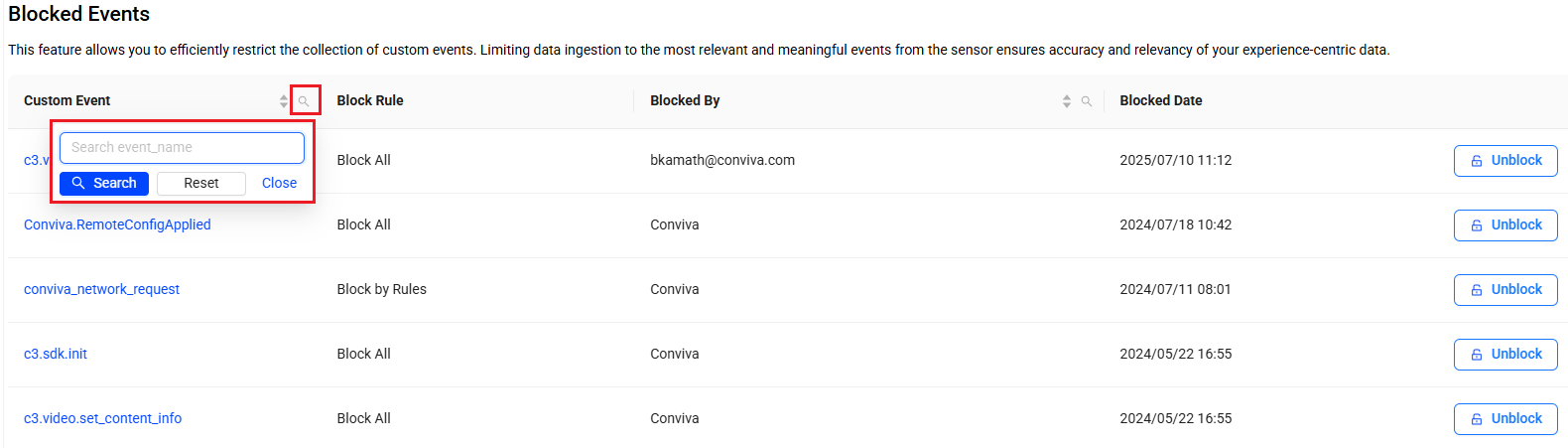
-
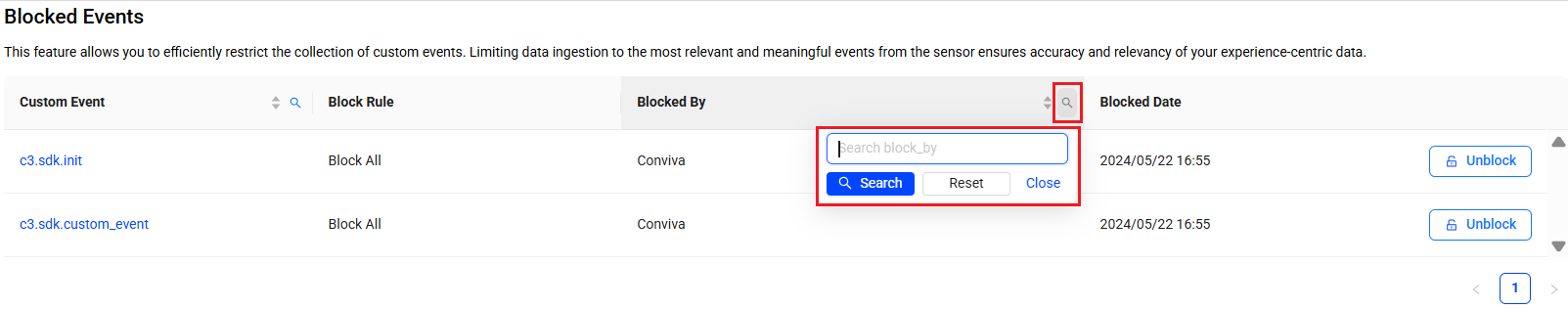
To find a blocked event by the blocked by user, click the search icon adjacent to the Blocked By column, enter part of the user's name in the search window, and click Search.
Editing Blocked Events
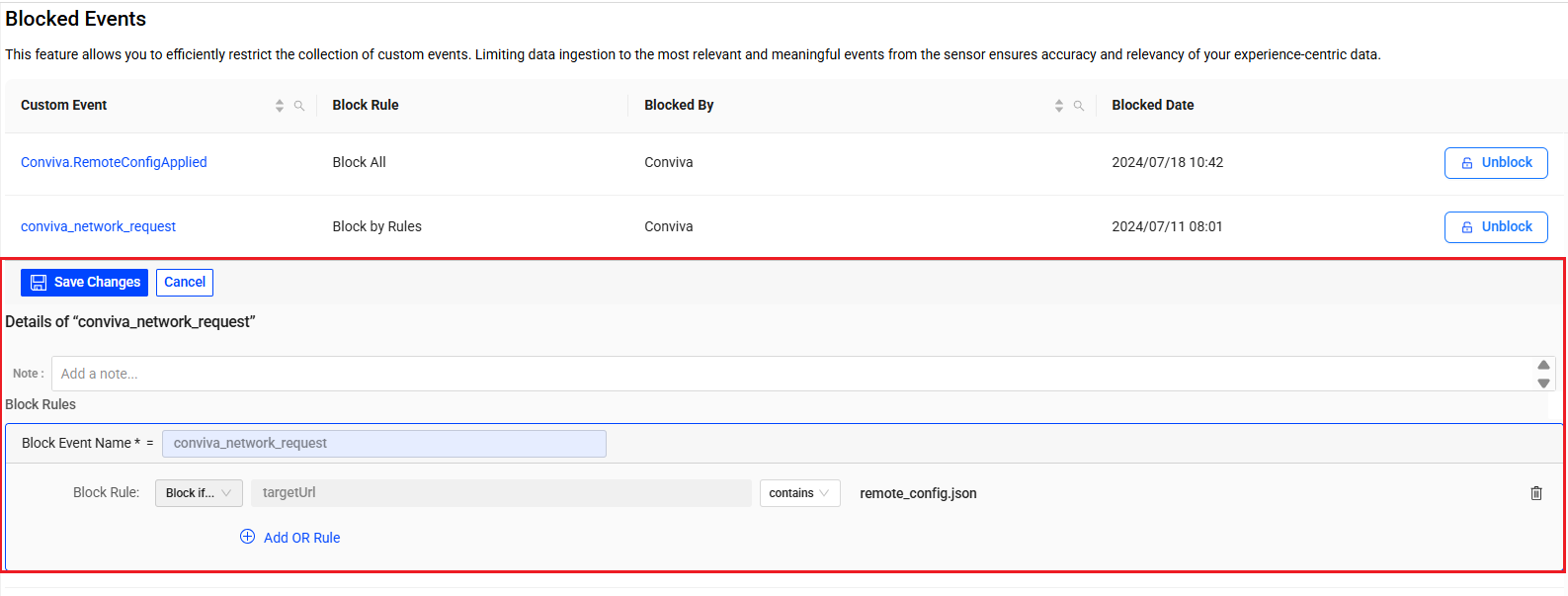
Change the block rule and note for an existing blocked event.
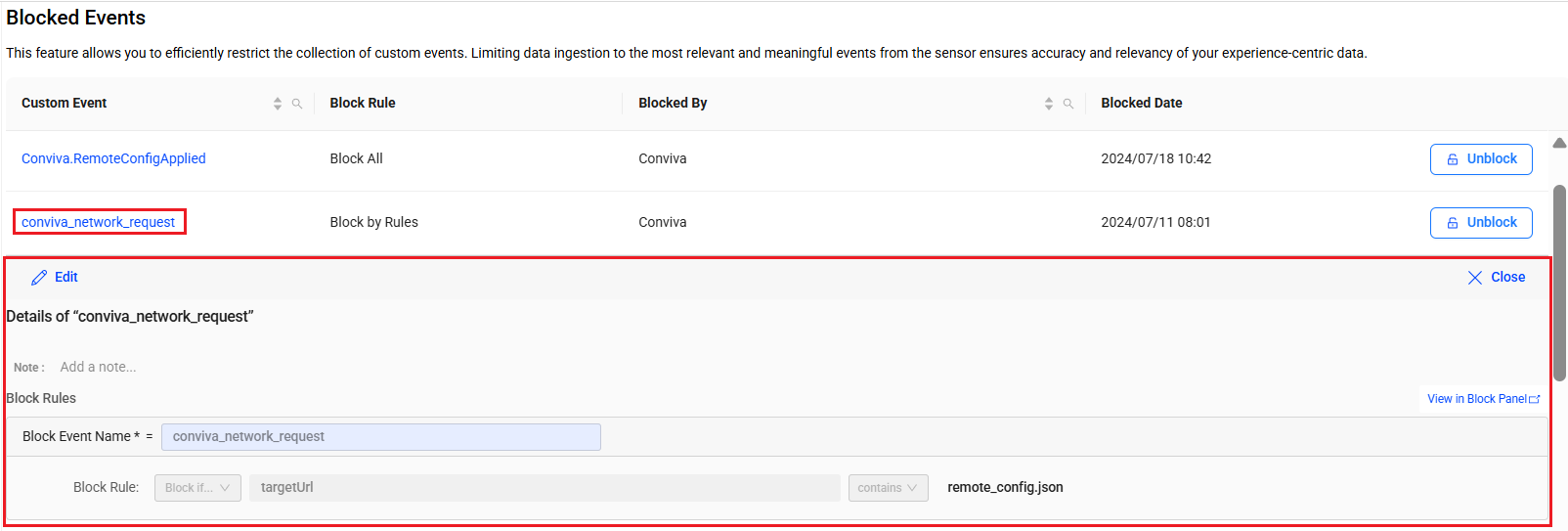
-
Click an event name under the Custom Event column to see details of the block events.
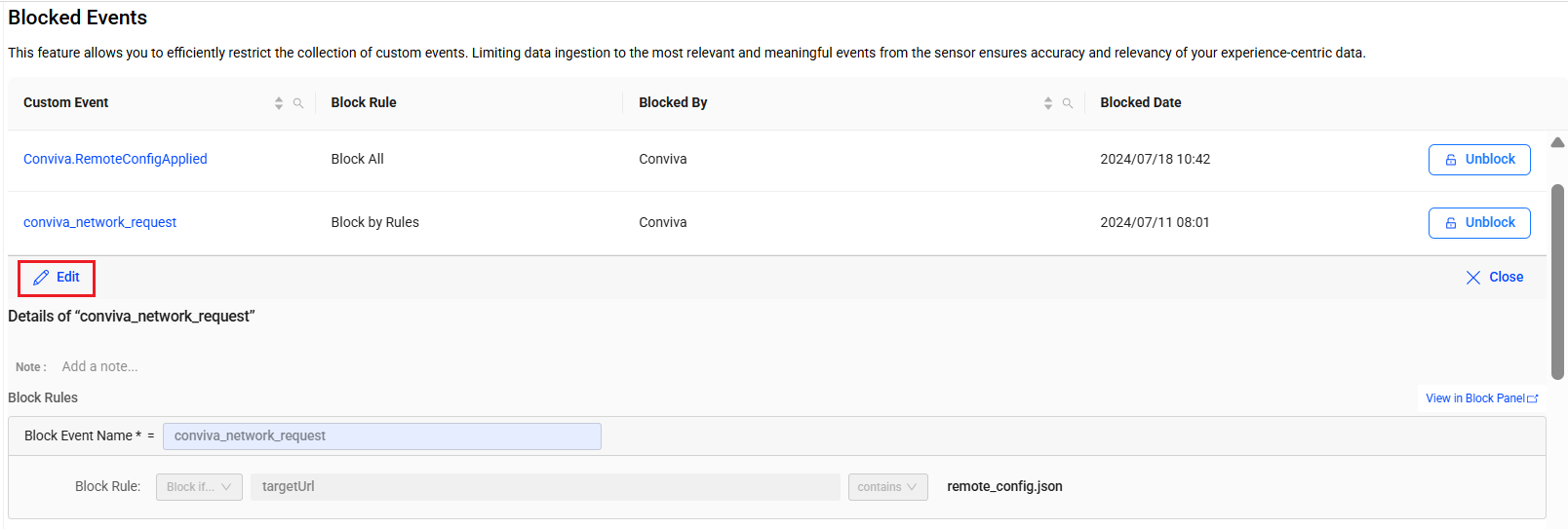
-
Click Edit in the event details section.
-
Change the block rule and/or update note, and click Save Changes.
Viewing Events in Block Panel
View a blocked event in Semantic Mapper page.
-
Click an event name under the Custom Event column to see details of the block event.

-
Click View in Block Panel in the event details section to see the blocked events related dimensions in the Semantic Mapper page.
Unblocking a Blocked Event
Unblock an existing blocked events to resume the event collection via ConvivaDPI sensor.
-
Click the Unblock button corresponding to the blocked event, and click Yes on the confirmation message pop-up.
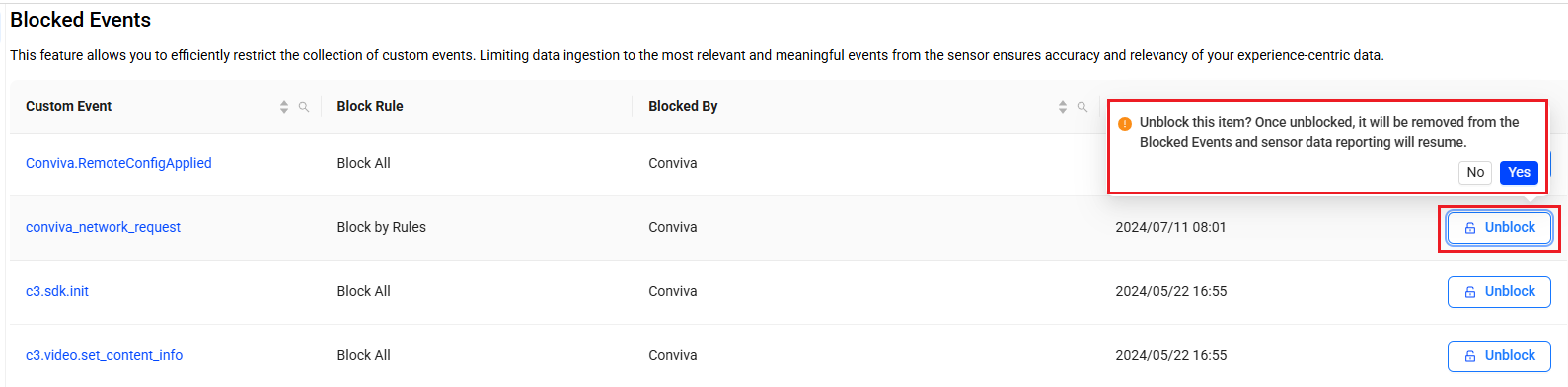
After unblocking an event, it is removed from the Blocked Events list and Conviva DPI sensor starts collecting the respective event data from the integrated app.
 Configured Network Request
Configured Network Request
Configure Network Request allows defining the collection rules for conviva_network_request events. When the rules are configured, the Conviva sensor collects network request events accrding to the matched rules. Select the collected events as raw data for mapping, if necessary.
Configure the network request data collection rules for multiple categories, such as metadata usage, EMP query fields, GraphQL, tag value, and metrics API.
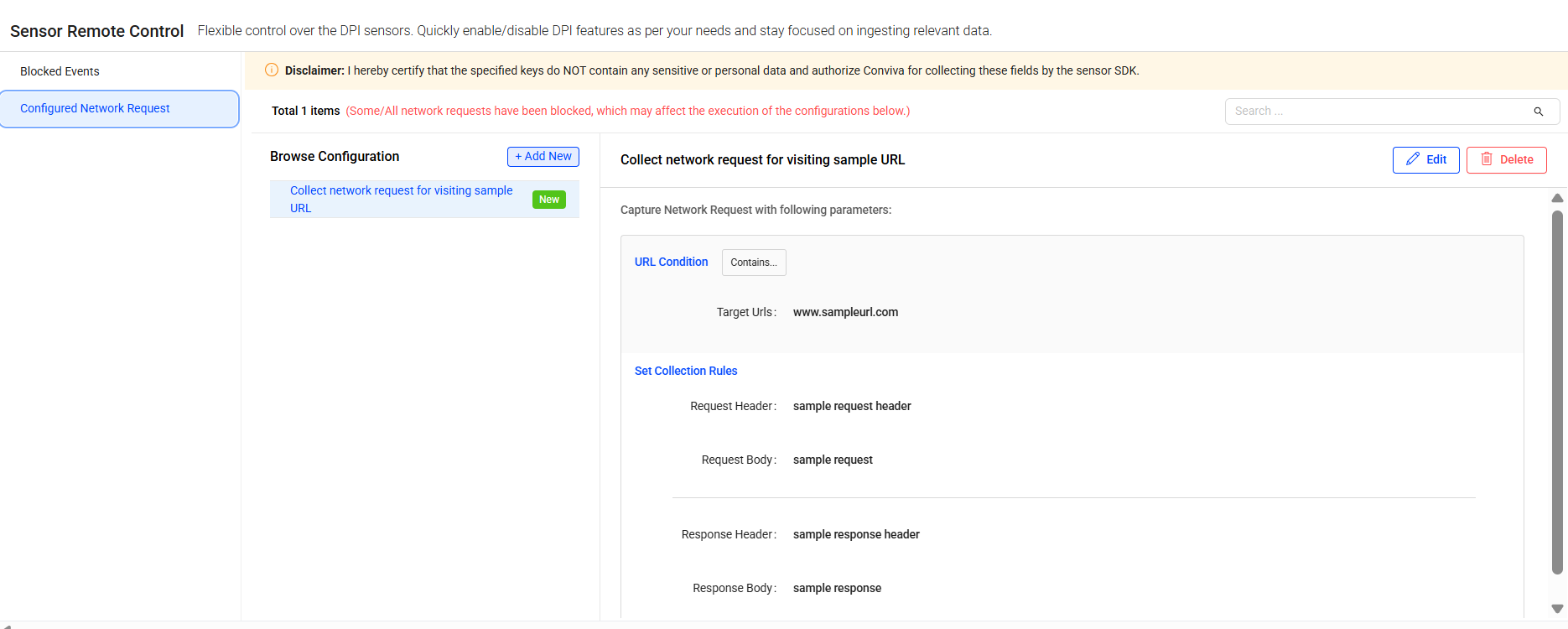
Collection Rule Order
Network request collection rules are applied based on the most recently changed rules, and then rules following the displayed category order. If a network request does not meet any configured rules in a category, the collection rule matching process stops and that network request data is not passed to DPI.
There are two methods for collecting conviva_network_request events:
-
Blocked events: blocks events matching blocked event criteria and collects all other conviva_network_request events.
-
Collection rules: collects events matching allowed event criteria and blocks all other conviva_network_request events.
Note: Events matching the blocked events criteria are blocked even if they also match any collection rules.
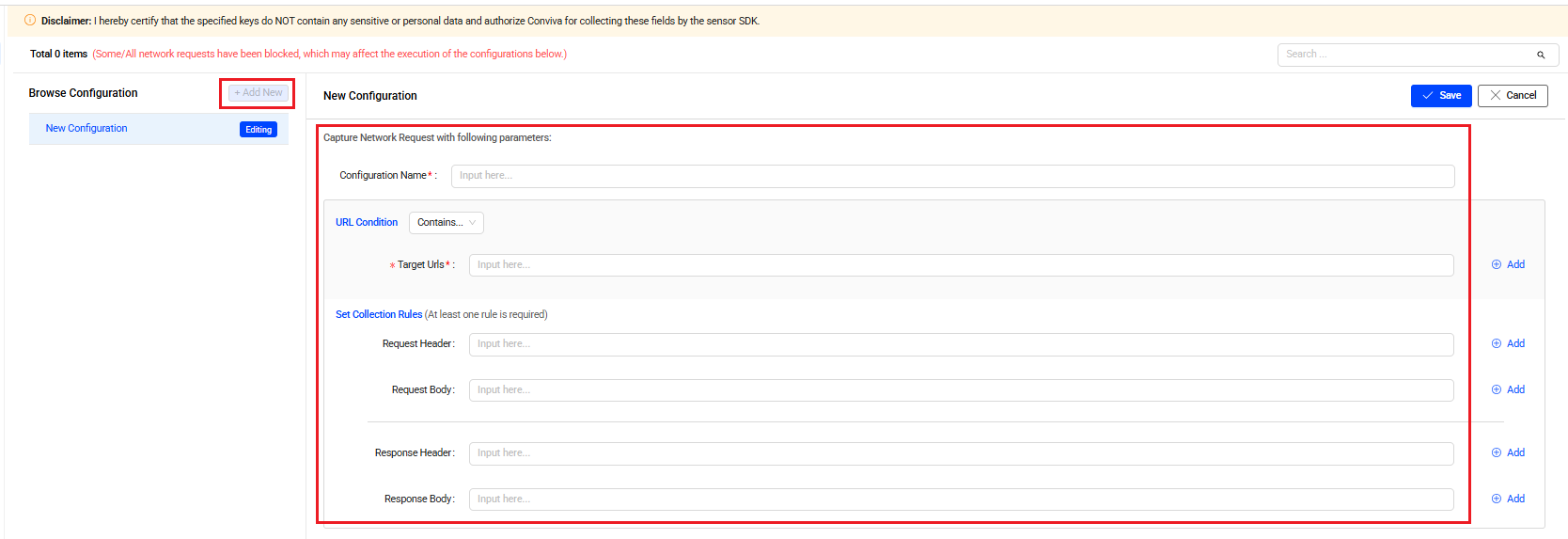
Creating Collection Rules
-
Click Add New in the Browse Configuration section, on the left pane.
-
Set the collection rule in the New Configuration secion, on the right pane:
-
Condition Name: Type a name for the collection condition.
-
Define the URL Conditions by selecting:
-
All: Enables rules to take effect on all conviva_network_request events.
-
Contains: Enables rules to take effect on events containing the Target Urls.
-
-
Set collection rules using Request Header, Request Body, Response Header, Response Body, separately.
Note: Click Add to include more rules if necessary.
 Example
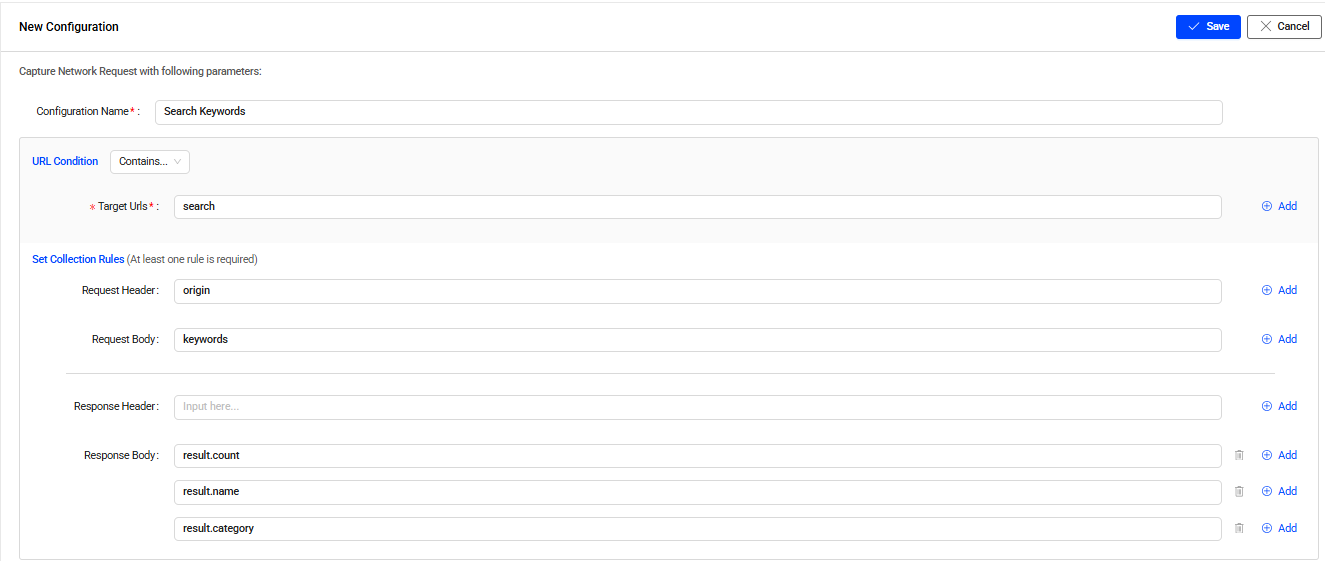
Example
Suppose you want to gather information about the keywords users search for and conduct in-depth analysis based on that information. To obtain the necessary data, you need to collect the relevant conviva_network_request events.
-
Configuration Name: Search Keywords
-
URL Condition: Select Contains and type search in the Target Urls field. This is required.
-
Set Collection Rules with:
-
origin as Request Heade.
-
keywords as Request Body.
-
Leve the Response Header field empty.
-
result.count, result.name, and result.category as Response Body.
-
-
-
Click Save. Conviva DPI sensor starts collecting the conviva_network_request events that match the rules.
 Auto Collection of Clicks
Auto Collection of Clicks
Customize the user-click tracking across the application, beyond tracking the click events for buttons and links. This section consists of two tabs, Collect Attributes and CSS Selectors. Use the default attributes and CSS selectors, and also create additional custom tags, CSS selectors, and attributes to track user clicks for various purposes, such as defining Out-of-Box (OOB) metrics, resolving UX issues, and even creating meaningful user Flows.
Note: This feature is available only for the DPI Web (JavaScript) Sensor version 1.1.15 and above. Conviva recommends updating the sensor to its latest version.
Use the toggle button at the section header to enable/disable this feature for the DPI sensor.
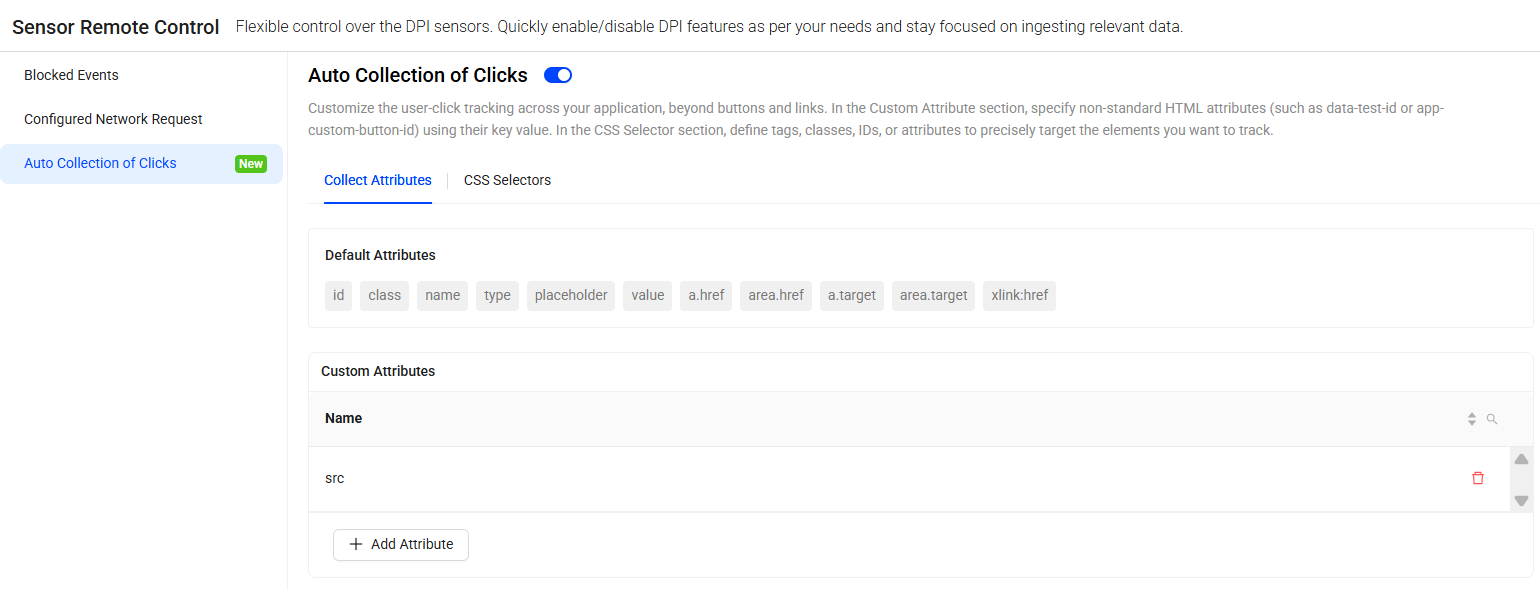
Collect Attributes
Specify the non-standard HTML attributes (such as data-test-id or app-custom-button-id) using their key value. By default, DPI sensors support collecting user-click events for certain attributes, such as, id, class, name, type, placeholder, value, a.href, area.href, a.target, area.target, and xlink:href.
In the Custom Attributes section, click the Add Attribute button to track user clicks on more custom attributes such as, src, title, alt. Click the Save button to deploy.
Note: Sensors may take 30 minutes to reflect the changes.
CSS Selectors
Define tags, classes, IDs, or attributes to precisely target the elements you want to track. By default, DPI sensors support collecting user-clicks for the native clickable selectors, such as button, a, select, textarea, input:not([type="hidden"]), summary, video, and audio.
In the Default Virtual Clickable Selectors section, use the toggle button to enable/disable the pre-defined click tracking for the virtual selectors.
In the Custom CSS Selectors section, click the Add CSS Selector button to specify the custom CSS Tag or custom CSS attribute for click tracking.
-
To define custom CSS tag:
-
Click the Add CSS Selector button.
-
Select the option Tag from the drop-down list.
-
Specify tag name in the adjacent field.
-
Click Save to deploy.
-
Note: Sensors may take 30 minutes to reflect the changes.
-
To define custom CSS attribute:
-
Click the Add CSS Selector button.
-
Select the option Attribute from the drop-down list.
-
Specify attribute name in the adjacent field.
-
Select a condition (Starts With, Ends With, Equals, and Contains) from the drop-down list.
-
Specify the value to match based on the selected condition.
-
Click Save to deploy.
-
Note: Sensors may take 30 minutes to reflect the changes.
For more information about Auto Collection of Clicks, see Sensor Remote Control.
 Cohort Replay (Beta)
Cohort Replay (Beta)
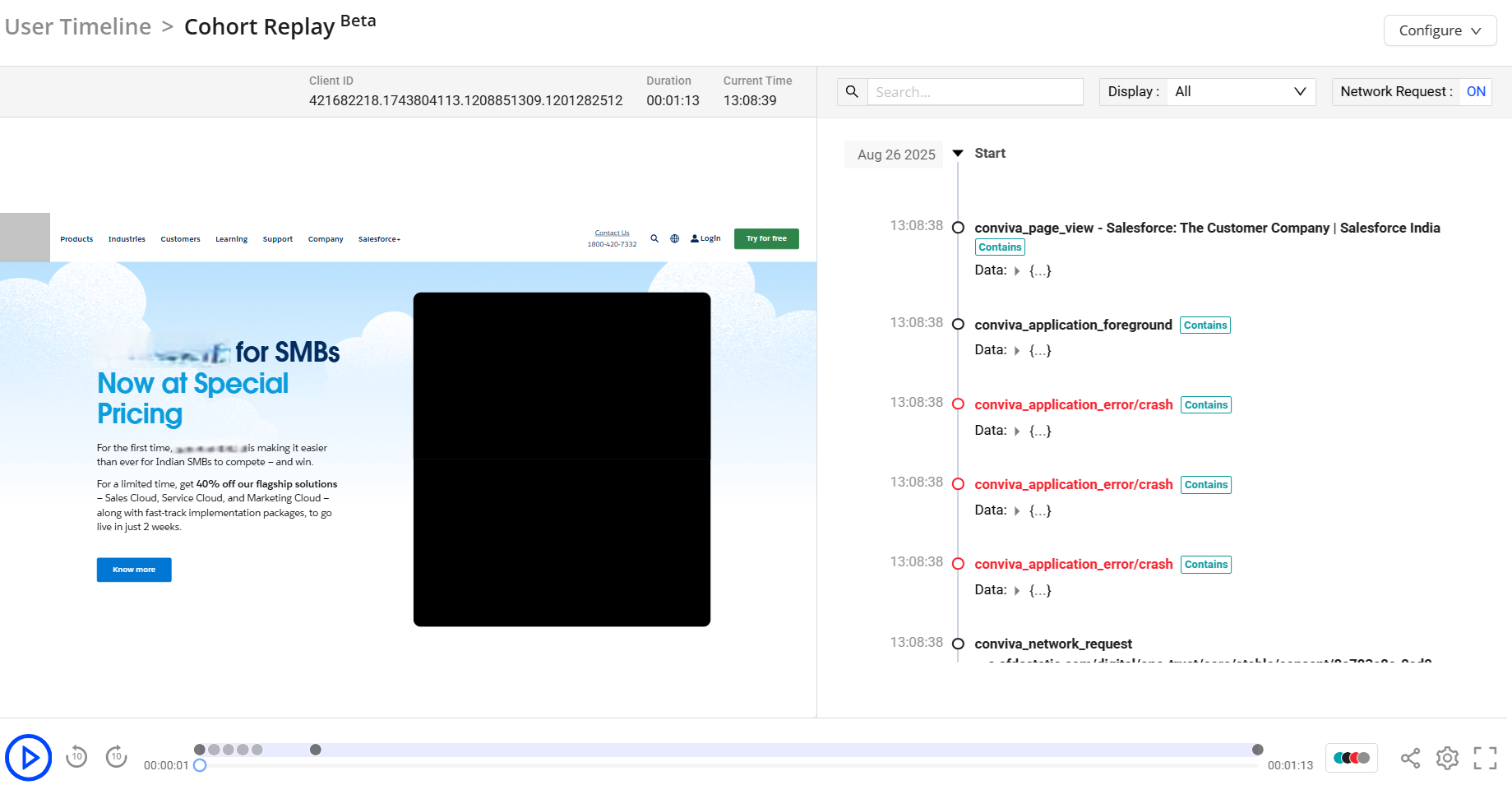
Cohort Replay enables the visual reconstruction and review of user navigations and actions within a customer's app. This feature captures how users interact with the app, including clicks, navigation, scrolling, media engagement, and text input, and then replays these interactions in a video-like experience. Cohort Replay provides direct visibility into how customers interact with digital platforms and user behaviors, based on a sampling percentage of user sessions. For data compliance, Conviva applies configurable masking levels (light, medium, or advanced) to protect Personally Linked/Locatable (PLL) data.
Note: Cohort Replay is disabled by default. As a prerequisite, customers must upgrade to the latest sensor version. To enable and use cohort replay, contact your Conviva representative to configure the sensor remote control settings, adjust the sampling percentage, and set the masking level according to your specific application requirements.
Supported Platforms and Versions: Web (JS) version 1.4.3 and above.
Use Cohort Replay to:
-
Understand the details in user behaviors and friction points
-
Link from Funnel and metric anomalies to visual behavior representations for quick user behavior optimizations.
-
Analyze the impact of user experience on flagged AI Alerts and check for anomalies.
-
Monitor the exact sequences of user actions to analyze behavior and UI improvements.
Launching Cohort Replay
Access the Cohort Replay from the Trends or Users Dashboard,
-
Navigate to Trends >> Cohort Replay Tab
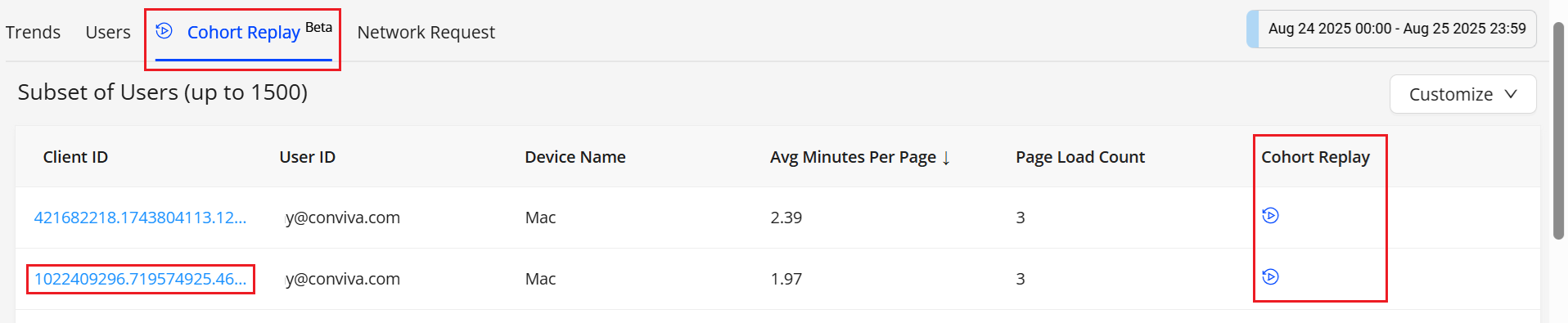
-
Click a Client ID or Cohort Replay icon associated with the user session to see the session details in a new User dashboard tab.
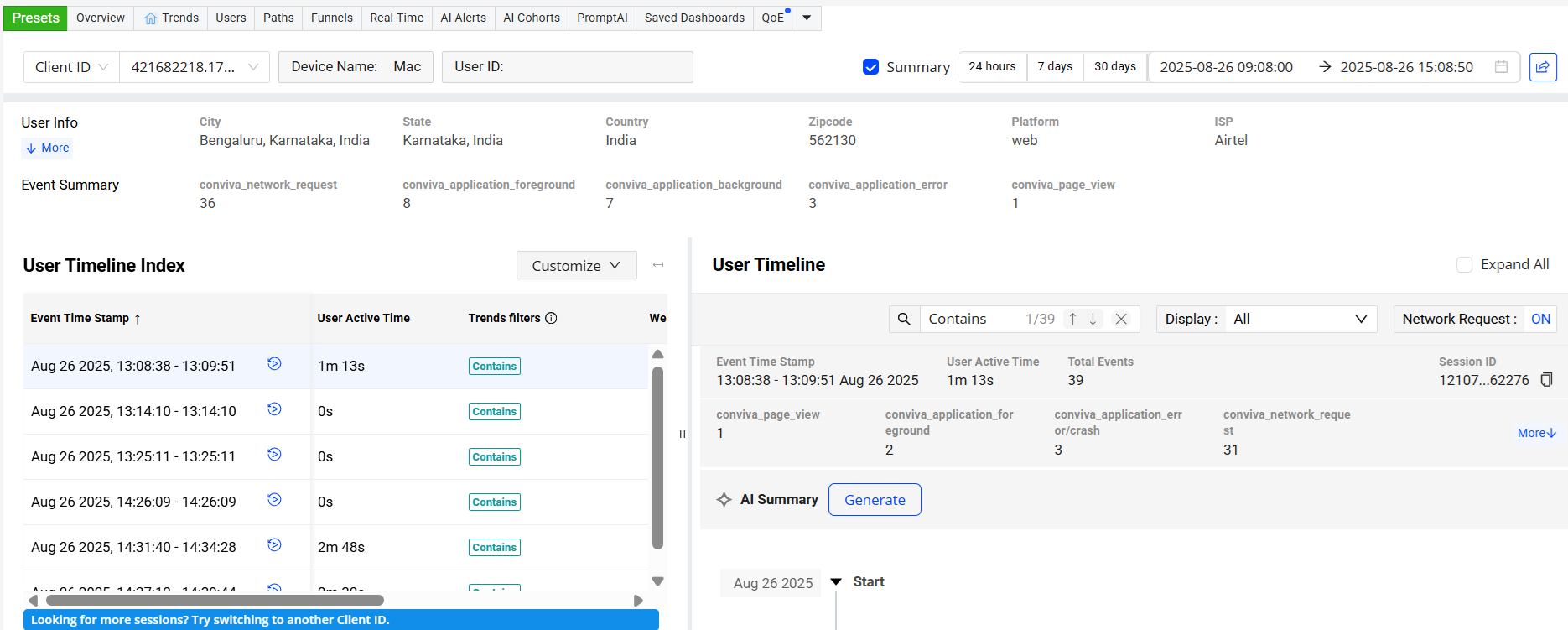
-
On the Users timeline, click the Cohort Replay icon adjacent to the Event Time Stamp to see the user timeline details with the cohort replay.

The player enables detailed session analysis through the following features:
-
Events Indicator: Colored dots display events, network requests, and errors. Hover the legend next to the share button to see the different types of events associated with the User Timeline.
-
Playback Controls: Options are provided to pause playback, seek to a specific position, fast forward by ten seconds, and rewind by ten seconds.
-
Session Sharing: Share the sessions for collaborative investigation of issues.
-
Settings: Speed control options allow adjustment of playback speed.
These capabilities support precise navigation, issue identification, and collaborative troubleshooting.
-
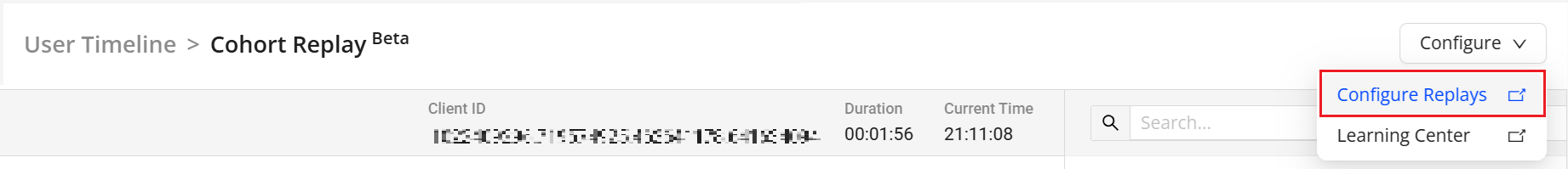
-
On the Cohort Replay screen, click the Configure drop-down and select Configure Replays to view the Cohort Replay configuration page in Sensor Remote Control.
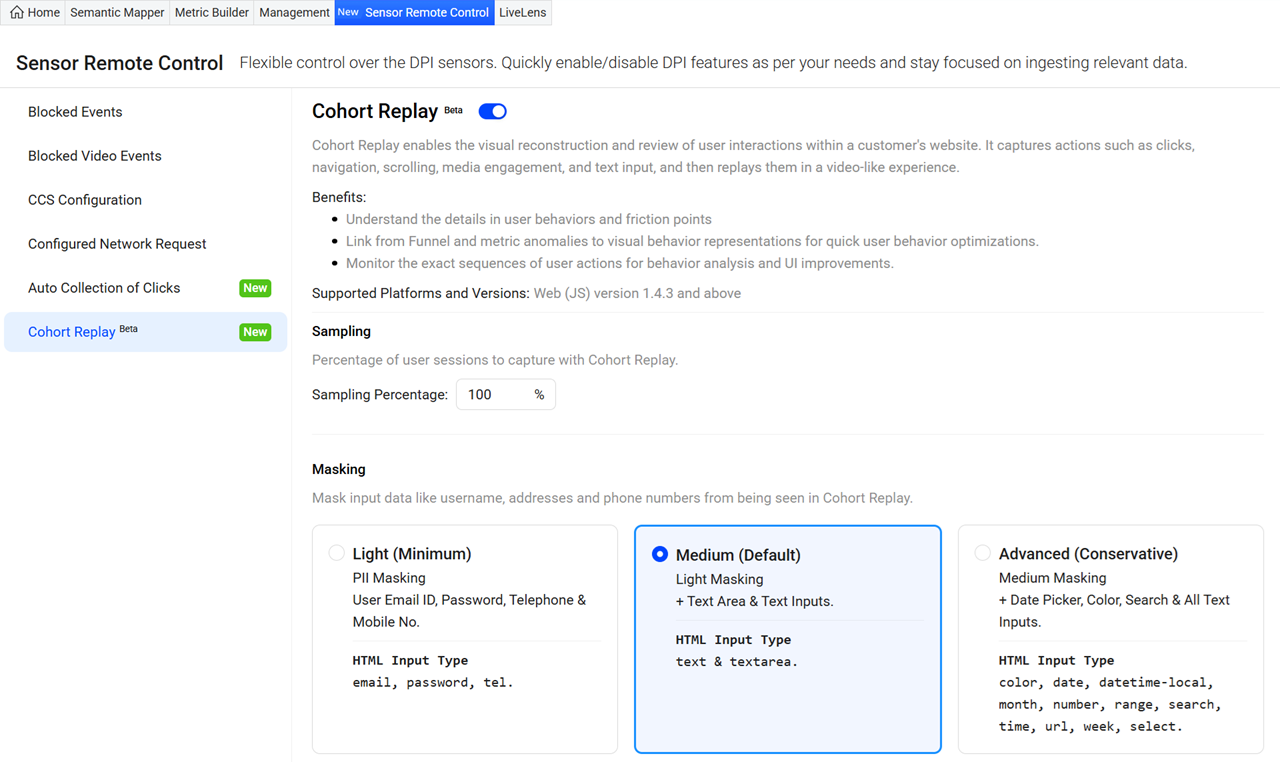
Configuring Cohort Replay
Use the Session Remote Control tab to enable the Cohort Replay, which allows to set the sampling percentage to specify the proportion of user sessions captured for Cohort Replay, and define the masking level to secure the PLL data.
-
Cohort Replay: Toggle to start recording the user sessions based on the specified sampling percentage, with the capability to replay the sessions.
-
Sampling: The sampling percentage specifies the proportion of user sessions captured for Cohort Replay. The value entered in the Sampling Percentage field determines the percentage of sessions recorded.
-
Masking: Conviva offers a data masking feature to ensure the security of Personally Linked/Locatable (PLL) data during session recordings. When this feature is enabled, sensitive information is not stored or exposed in recorded sessions. Conviva supports different configurable masking levels, allowing customers to strike a balance between data protection and operational visibility. This setting provides robust protection while maintaining operational visibility.
There are three levels of masking:
-
Light (Minimum): The cohort replay does not capture any user email IDs, passwords, telephone numbers, or mobile numbers.
-
Medium (Default): In addition to the Light masking, the cohort replay does not capture text or text areas. Conviva recommends the Medium masking level.
-
Advanced (Conservative): In addition to Medium Masking, the cohort replay does not capture the Date Picker, Color, Search, and All Text Inputs.
-
Use Cases
-
Cohort Replay provides visibility into funnel conversion and related metrics. It captures the exact user experience with visual context, enabling the identification of anomalies or performance deterioration that may impact business outcomes.
-
The timeline view provides a visual representation of the user experience, facilitating drill-down analysis and supporting the identification of friction points, as well as analyzing user behavior.
-
Cohort Replay links anomalies to the corresponding user sessions. It displays the related replay when you select an anomaly in AI Alerts, providing a detailed analysis of user behaviour associated with the anomaly.
Technical Features and Limitations
During this beta release,
-
Input Masking: While the system masks sensitive fields (passwords, emails, text, etc.) by default, it does not yet mask Date, Month, Range, Time, or Week inputs; instead, it replaces them with static placeholder values (e.g., dd/mm/yyyy for Date).
-
For any static resources that are required to be downloaded from a remote server, cross-origin access is required.
-
Does not support cohort replay for full-screen video playback using the native <video> element.
Cohort Replay supports navigation through multiple tabs and subdomains, providing a seamless playback experience during replay sessions.
-
Recording Persistence
-
Incomplete Uploads: If a user closes the application or browser before the recording has been uploaded, the corresponding session content will not be visible in Pulse. Recording resumes only when the browser or application is relaunched.
-
Remote Disablement: If recording is disabled remotely (through configuration) after a session has been captured, there is a risk of losing up to the last one minute of replay data.
-
-
Performance and Rendering Constraints.
-
UI Rendering Behavior: Lazy-loaded interfaces may cause playback inconsistencies, including occasional overlaps or artifacts in the recorded session.
-
Event Volume Limit: Automatically discards recorded events once the event count exceeds 5,000 entries, which may truncate longer or more interaction-heavy sessions.
-
-
Content Capture Gaps
-
PDFs Not Recorded: Content rendered within PDF viewers is not captured and do not appear in cohort replay playback.
-
Shadow DOM:
-
Does not capture inputs within the open Shadow DOM.
-
Does not capture elements in the Closed shadow DOM and therefore remains invisible to replay.
-
-
-
This beta release supports Cohort Replay for web applications only. Cohort Replay for mobile devices is not available in this release.
-
Sampling percentage and masking levels are read-only within the platform interface. Contact your Conviva Representative for setting adjustments.
-
Cohort Replay does not support session recordings with Canvas and other player interaction tools.
-
Session recordings do not support session recordings of web applications embedded with multiple <iframe> elements.